
Image may differ from product. See technical specification for details.
Search for the bearing model you need
Standard
GB,ASTM/AISI,ГОСТ,BS,JIS,NF,DIN / VDEh,DIN / VDEh
Screw shaft outer diameter (d)
15mm-55mm
Lead (Ph)
10mm-50mm
Ball center-to-center diameter (dp)
15.75mm-57mm
Material
Carbon Steel, Bearing Steel, Stainless Steel
Brand
QIBR/OEM/Neutral
Package
QIBR/Standard Industrial Package/OEM
Applications
Machine Tools, Precision Instruments, Semiconductor, Aerospace, Printing Machinery, Medical Devices
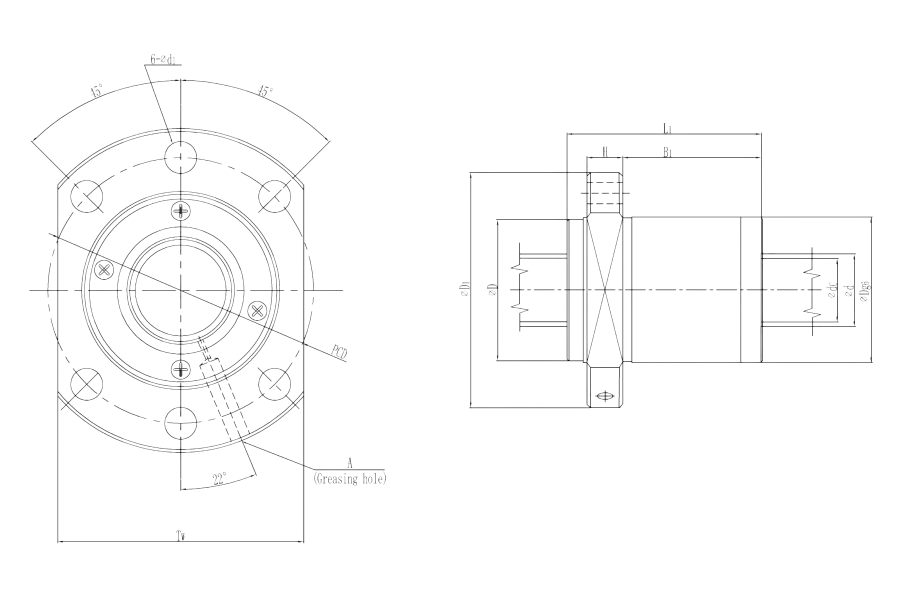
| NO. | Product | Product Number | Ball center-to-center diameter (dp) | Lead (Ph) | No. of loaded circuits rows X turns | Screw shaft outer diameter (d) | Thread minor diameter (dc) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |

|
SBK 1520-3.6 | 15.75 mm | 20 mm | 1X1.8 | 15 mm | 12.2 mm |
| 2 |

|
SBK 1616-3.6 | 16.65 mm | 16 mm | 1X1.8 | 16 mm | 13.5 mm |
| 3 |

|
SBK 2010-5.6 | 20.75 mm | 10 mm | 1X2.8 | 20 mm | 17.2 mm |
| 4 |

|
SBK 2020-3.6 | 20.75 mm | 20 mm | 1X1.8 | 20 mm | 17.2 mm |
| 5 |

|
SBK 2030-3.6 | 20.75 mm | 30 mm | 1X1.8 | 20 mm | 17.2 mm |
| 6 |

|
SBK 2520-3.6 | 26 mm | 20 mm | 1X1.8 | 25 mm | 21.5 mm |
| 7 |

|
SBK 2525-3.6 | 26 mm | 25 mm | 1X1.8 | 25 mm | 21.5 mm |
| 8 |

|
SBK 3220-5.6 | 33.25 mm | 20 mm | 1X2.8 | 32 mm | 27.9 mm |
| 9 |

|
SBK 3232-5.6 | 33.25 mm | 32 mm | 1X2.8 | 32 mm | 27.9 mm |
| 10 |

|
SBK 3620-7.6 | 37.75 mm | 20 mm | 1X3.8 | 36 mm | 30.4 mm |
| 11 |

|
SBK 3636-5.6 | 37.75 mm | 36 mm | 1X2.8 | 36 mm | 31.4 mm |
| 12 |

|
SBK 4020-7.6 | 42 mm | 20 mm | 1X3.8 | 40 mm | 34.1 mm |
| 13 |

|
SBK 4030-7.6 | 42 mm | 30 mm | 1X3.8 | 40 mm | 34.1 mm |
| 14 |

|
SBK 4040-5.6 | 42 mm | 40 mm | 1X2.8 | 40 mm | 34.9 mm |
| 15 |

|
SBK 5020-7.6 | 52 mm | 20 mm | 1X3.8 | 50 mm | 44.1 mm |
| 16 |

|
SBK 5030-7.6 | 52 mm | 30 mm | 1X3.8 | 50 mm | 44.1 mm |
| 17 |

|
SBK 5036-7.6 | 52 mm | 36 mm | 1X3.8 | 50 mm | 44.1 mm |
| 18 |

|
SBK 5050-5.6 | 52 mm | 50 mm | 1X2.8 | 50 mm | 44.9 mm |
| 19 |

|
SBK 5520-7.6 | 57 mm | 20 mm | 1X3.8 | 55 mm | 49.1 mm |
| 20 |

|
SBK 5530-7.6 | 57 mm | 30 mm | 1X3.8 | 55 mm | 49.1 mm |
| 21 |

|
SBK 5536-7.6 | 57 mm | 36 mm | 1X3.8 | 55 mm | 49.1 mm |
Features and advantages of SBK series ball screws
The SBK series ball screw has many significant features and advantages, playing a key role in various fields, mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. High efficiency
The working principle of the SBK series ball screw is that the steel balls roll inside the screw threads and nuts, reducing friction, so the transmission efficiency is higher.
2. Low friction and long life
The SBK series ball screw transmits power through rolling friction rather than sliding friction, so it has a lower friction coefficient, reduces energy loss, and has less wear and tear, extending its service life. The rolling friction when the ball contacts the thread generates much less heat than sliding friction and lowers the temperature rise, thus improving its durability and stability.
3. High precision
The SBK series ball screws can achieve high-precision motion control and are often used in applications that require precise positioning, such as CNC machine tools, precision instruments, etc.
4. Higher load capacity
Because the steel ball rolls between the screw and the nut, it can share a larger load. Compared with traditional linear bearings, the SBK series ball screw has a stronger load-bearing capacity. This makes it suitable for mechanical transmission applications requiring larger loads.
The performance improvement and solutions of ball Screw SBK Series
1. Improve accuracy
By using high-precision processing equipment (such as CNC machine tools, grinders, etc.), it is possible to ensure that the geometry, dimensional accuracy and surface roughness of the screw and ball track reach a higher level.
2. Reduce friction and improve transmission efficiency
The usage of high-performance lubricants and greases can reduce friction, improve transmission efficiency, reduce temperature rise and extend service life.
Improve the lubrication design of the ball track: By rationally designing the contact angle and contact method between the ball and the track and adopting an appropriate lubrication system, it is possible to reduce wear while ensuring efficiency.
3. Torsion resistance and stability
The bending and torsion resistance of ball screws can be improved by improving the size ratio of the screw or using high-strength materials.
4. Self-locking design
The ball screw adopts a self-locking design, which can automatically lock when there is no load or a small load, reducing the free movement of the system when it stops and improving the stability of the system.
Main application areas of ball screw SBK series
1. CNC machine tools
Ball screws are used in feed systems in CNC machine tools to provide high-precision positioning and motion control.
2. High-end logistics equipment
In high-end automated logistics systems, the SBK series ball screws can provide precise and efficient linear transmission and are used in automated stackers, high-bay warehouses, automatic conveying systems and other fields. Their quick response and high transmission efficiency enable logistics equipment to complete large-scale material handling tasks in a short period of time.
3. Medical devices
In some medical devices, the SBK series ball screws can help the medical equipment to accurately position and adjust, ensuring the efficiency and precision of the treatment or detection process.
4. Industrial Automation
Large lead ball screws are widely used in industrial automation equipment, especially in linear transmission systems that require fast and high precision.


