Newsroom
Correct Method for Replacing Deep Groove Ball Bearing
Deep groove ball bearing (GB/T 276—2003), formerly known as single-row radial ball bearings, are the most widely used type of rolling bearings. They are characterized by low friction resistance and high rotational speed. The main models include: SKF 6203-2Z/VA208, SKF W61096-2Z, FAG 6209-TB-P6-C3, SKF 6314M/C4VL0241, NSK 6326ZZSC3NS7S5, etc. They can be used in mechanical parts that bear radial loads or combined loads of both radial and axial forces, and can also be used in parts that bear axial loads, such as small-power motors, automobile and tractor gearboxes, machine tool gearboxes, general machinery, tools, etc.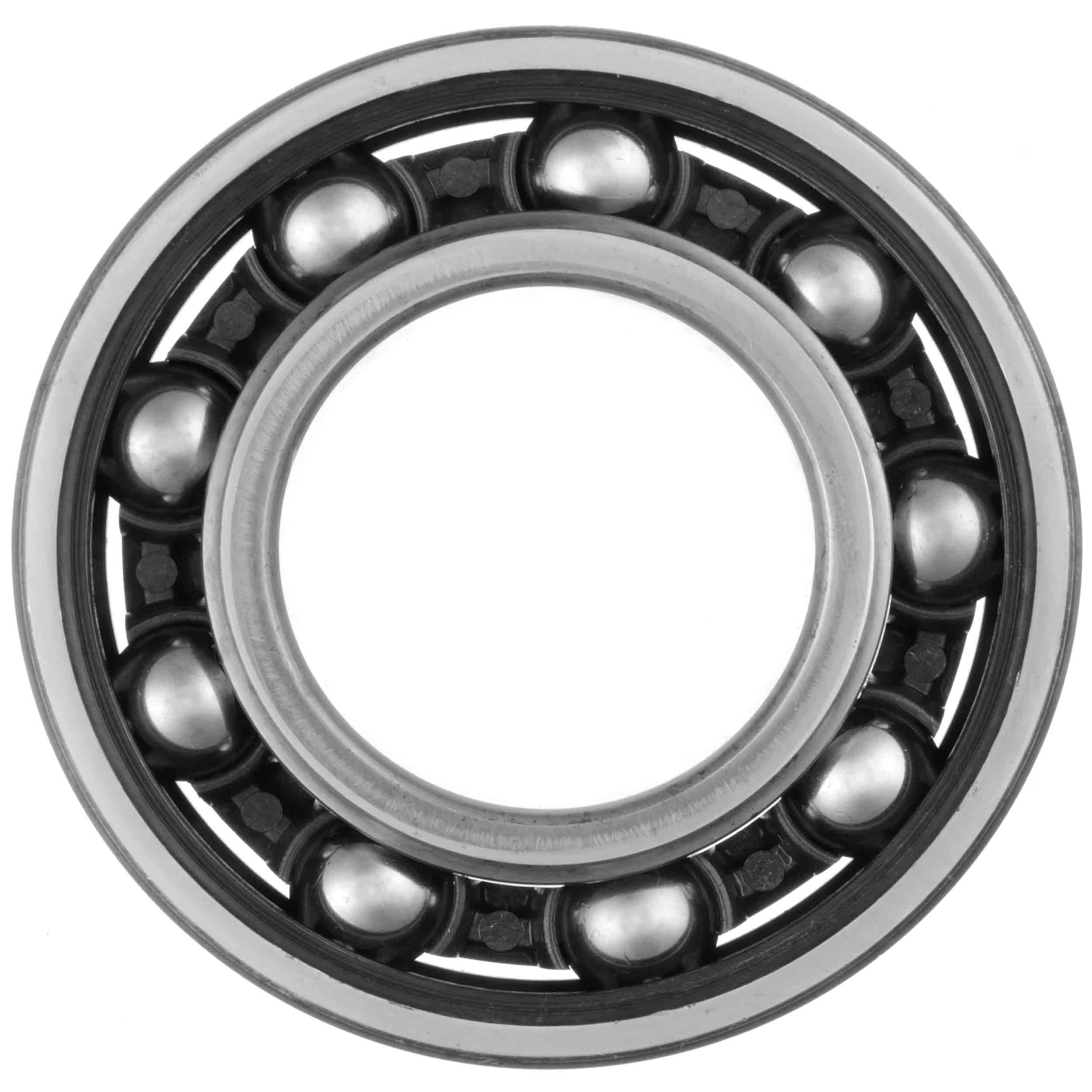 
Most deep groove ball bearing damages are caused by various factors—exceeding the originally estimated load, ineffective sealing, excessively small bearing clearance due to over-tight fitting, etc. Each of these factors has its specific damage form and will leave special damage traces.
Why do bearings wear out? Only some deep groove ball bearing get damaged in practical applications.
1) Monitoring with simple tools
There are many types of abnormal sounds from deep groove ball bearing, which are difficult to describe in words and mainly rely on accumulated experience. The normal operating sound of imported bearings should be uniform, stable, and not harsh, while abnormal bearing operating sounds are intermittent, impactful, or harsh in various ways. First, one should get used to the normal bearing operating sound, then be able to judge abnormal bearing sounds. Through the accumulation of practical experience, dealers of German imported bearings can further analyze what kind of abnormal sound corresponds to what kind of abnormal bearing phenomenon.
In situations where the above instruments are not available, operators can hold a round rod, wrench, or other tools against the part of the machine housing close to the bearing, place their ear on the tool to monitor the bearing operating sound transmitted through the tool. Of course, a modified medical stethoscope can also be used. 
2) Using deep groove ball bearing working condition monitoring instruments
Using such instruments can make full use of the bearing's working potential, timely report the bearing for repair, and avoid faults, which is safe and economical.
For example, when using the HD-1 instrument, if the pointer approaches the danger zone from the warning zone and does not return after taking measures such as improving lubrication, it can be determined that there is a problem with the bearing itself. At this time, the bearing can be reported for repair before it enters the danger zone. How far from the danger zone to start reporting for repair can be adjusted based on experience. 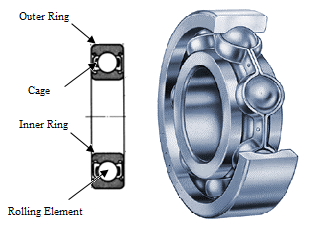
Using instruments such as ferrographs, SPM, or HD-1 bearing working condition monitoring instruments to judge the working status of bearings and determine when they should be reported for repair is a convenient and reliable method.


