Newsroom
What Are the Operating Characteristics and Industrial Applications of Precision Crossed Roller Bearings?
The structure of a precision crossed roller bearing is divided into an inner ring or an outer ring. After rollers and a cage are installed, it is firmly integrated with the crossed roller collar to prevent separation from each other. Moreover, the operation of installing the crossed roller collar is also very simple. Precision crossed roller bearings have some unique application characteristics.
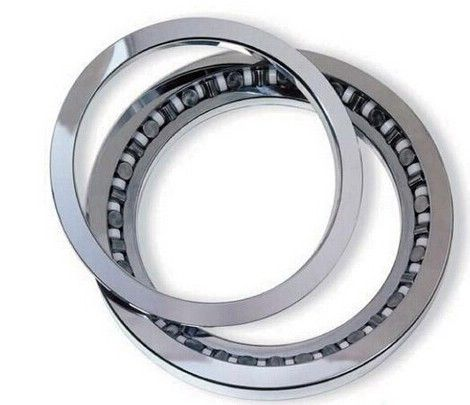

The rollers of precision crossed roller bearings are arranged in a crisscross pattern. Therefore, only one set of crossed roller collars can bear loads from all directions. Compared with traditional models, their rigidity is increased by 3 to 4 times.
Since the inner ring or outer ring of a precision crossed roller bearing has a two - split structure, the bearing clearance is adjustable. Even when a preload is applied, it can still achieve high - precision rotational movement.

Precision crossed roller bearings can bear loads from all directions at the same time, such as axial loads, thrust loads or moment loads. Because the rollers are in linear contact with the surface of the raceway, the possibility of elastic deformation of the bearing under load is very small.
In a precision crossed roller bearing, cylindrical rollers are arranged perpendicular to each other by a cage on the 90 - degree V - shaped groove rolling surface. Thus, one set of precision crossed roller bearings can bear loads from all directions, including radial loads, axial loads and moment loads. 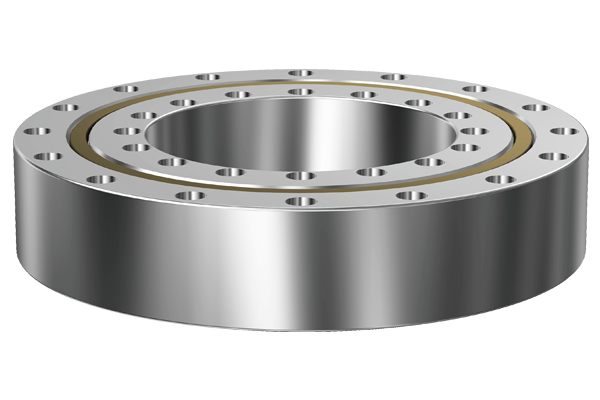
The sizes of the inner and outer rings are miniaturized to the greatest extent. Especially the ultra - thin type has a mini size close to the limit and high rigidity.
Precision crossed roller bearings are widely used in fields such as industrial robots, rotating worktables of machining centers, rotating parts of manipulators, ultra - precision rotating worktables, machine tools and medical equipment.


