Newsroom
Numerical control machine tools will use a variety of bearings
2024-09-19Numerical control machine tools will use a variety of bearings. The following are some common types:
I. Angular contact ball bearings
1. Characteristics
- They can bear radial and axial loads simultaneously.
- The size of the contact angle can be designed according to specific requirements. Different contact angles have differences in load-bearing capacity and axial stiffness.
- They have good performance at high-speed operation with a small coefficient of friction, which can meet the working requirements of high-speed cutting in numerical control machine tools.
2. Applications in numerical control machine tools
They are often used in the spindle components of numerical control machine tools. For example, at the front end of the spindle in a high-speed machining center, angular contact ball bearings are used in pairs or in multiple groups to provide high-precision rotational support for the cutting tools to ensure machining accuracy and surface quality.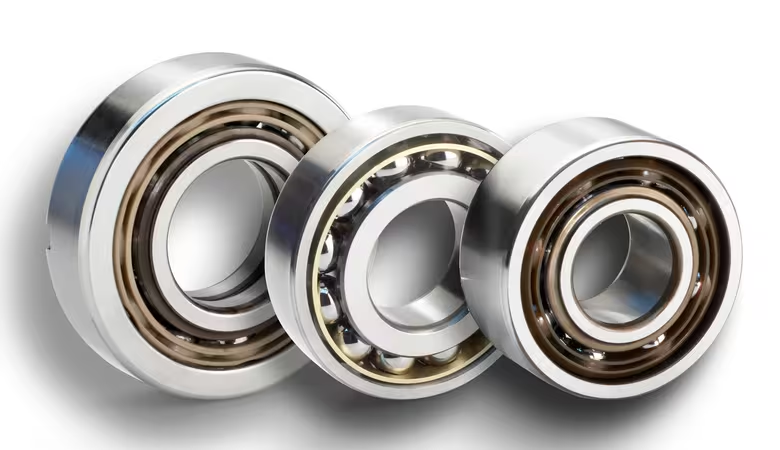 
1. Characteristics
- They can bear large radial and unidirectional axial loads simultaneously.
- The contact lines between the rollers and the raceways of the inner and outer rings converge at the axis of the bearing, making the load distribution more reasonable and having a strong load-bearing capacity.
- They have good rigidity and impact resistance.
2. Applications in numerical control machine tools
They are often used at the rear end of the spindle of numerical control machine tools and in some parts that bear large axial and radial forces. For example, in the spindle system of some heavy-duty numerical control machine tools, tapered roller bearings can be used in combination with angular contact ball bearings to meet the requirements for spindle support during heavy cutting processing of the machine tool.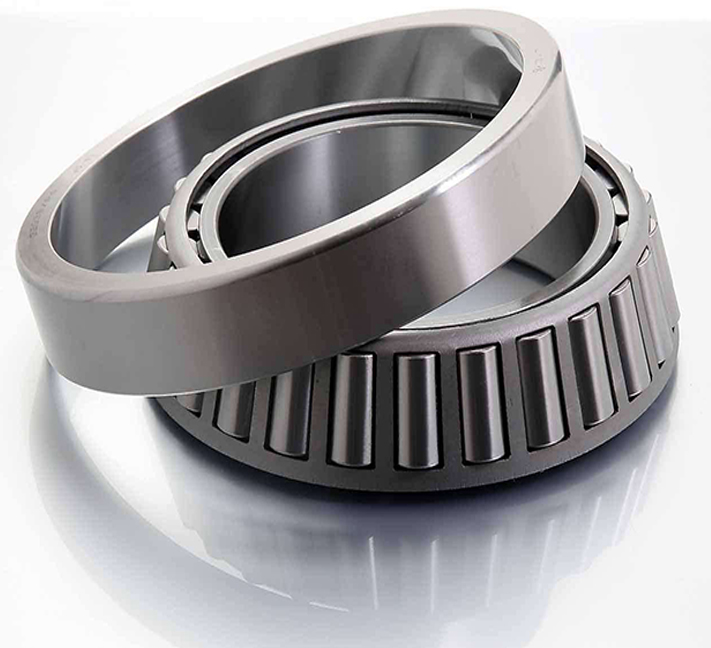 
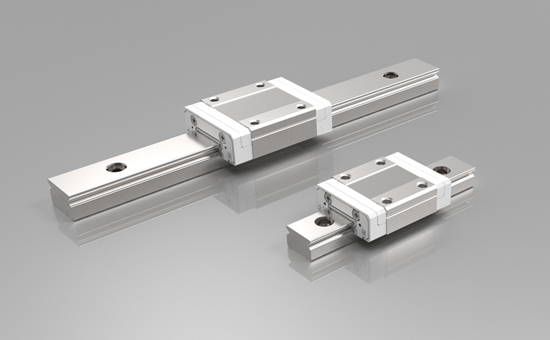
III. Ball linear bearings for linear guides
1. Characteristics
- They are specifically designed for linear motion with extremely small frictional resistance and can achieve high-precision linear motion.
- Multiple balls roll between the guide rail and the slider. The contact between the balls and the guide rail and the slider is a point contact, resulting in smooth motion.
- They have high positioning accuracy and repeat positioning accuracy, which can meet the requirements for the precise movement of coordinate axes during the processing of numerical control machine tools.
2. Applications in numerical control machine tools
They are widely used in the guide rail systems of various coordinate axes of numerical control machine tools. For example, on the X, Y, and Z coordinate axis guide rails of a numerical control milling machine, ball linear bearings can enable components such as the worktable and saddle to move accurately and smoothly along the guide rails, ensuring the positional accuracy of the cutting tool relative to the workpiece during the processing.
1. Characteristics
- They mainly bear radial loads and can also bear a certain amount of axial load.
- They have a simple structure, are convenient to use, and have a high cost-performance ratio.
- They have high operating accuracy and are suitable for occasions with high-speed rotation.
2. Applications in numerical control machine tools
They are widely used in the auxiliary transmission systems of numerical control machine tools. For example, in the tailstock sleeve of a numerical control lathe, the rotating shaft of the tool magazine in the automatic tool changer, and other parts, deep groove ball bearings can provide reliable support.


