Newsroom
What are 608 bearing dimensions?
The 608 bearing is one of the most widely used miniature bearings in the world, known for its compact size, versatility, and standardized dimensions. From skateboards to industrial machinery, this bearing plays a critical role in ensuring smooth rotational motion. In this article, we delve into the technical specifications, international standards, material options, and applications of the 608 bearing, providing a detailed overview for engineers, hobbyists, and industry professionals.

1. Basic Dimensions of the 608 Bearing
The 608 bearing belongs to the deep groove ball bearing family, designed to handle both radial and axial loads. Its dimensions follow a globally recognized numbering system:
“6” indicates the bearing type (deep groove ball bearing).
“0” signifies the outer diameter series (extra-light series).
“8” corresponds to the bore diameter (inner diameter) of 8 mm.
According to ISO (International Organization for Standardization) standards, the 608 bearing’s key dimensions are:
Bore Diameter (d): 8 mm
Outer Diameter (D): 22 mm
Width (B): 7 mm
Tolerances:
- Bore diameter tolerance: Typically ±0.005 mm.
- Outer diameter tolerance: ±0.01 mm.
- Width tolerance: ±0.1 mm.
Higher-precision variants (e.g., ABEC-5 or ABEC-7) feature tighter tolerances for applications requiring exceptional accuracy.
2. International Standards and Cross-References
The 608 bearing’s dimensions are standardized across major industrial regions, though naming conventions may vary slightly:
1. ISO Standard: 608 (universal designation).
2. JIS Standard (Japan): 608ZZ (the “ZZ” suffix denotes double metal shields).
3. DIN Standard (Germany): MR128.
4. ABEC Ratings: Defined by the Annular Bearing Engineers’ Committee (USA), ABEC grades (1–9) classify precision levels, with higher grades offering better rotational accuracy and speed capabilities.
Equivalent Models:
R8 (common in Europe).
8x22x7 (a non-standard size-based designation).
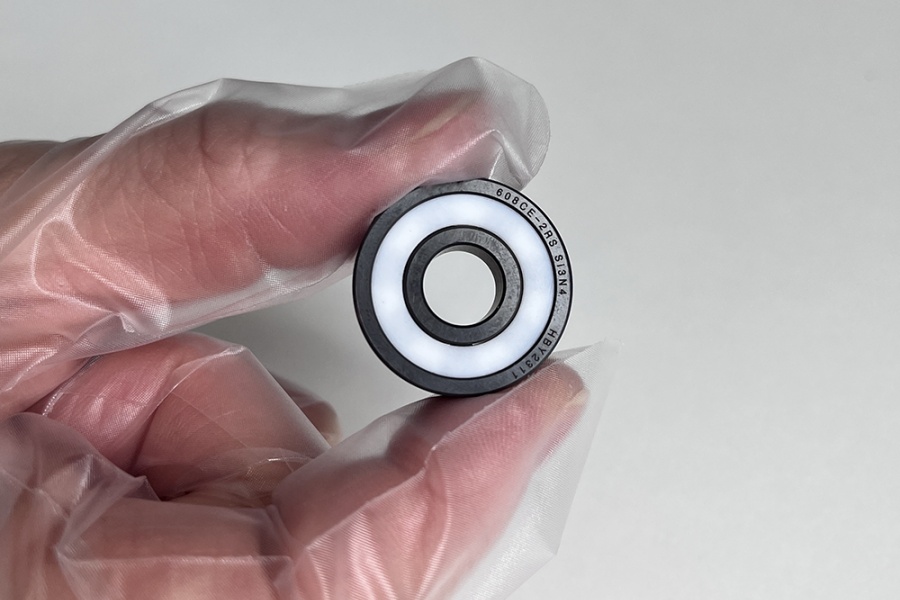

3. Material Options and Design Features
The performance of a 608 bearing depends heavily on its material and construction. Common configurations include:
A. Material Choices
Chromium Steel (GCr15): The standard material for 608 bearings, offering high hardness, wear resistance, and affordability. Ideal for general-purpose use in dry or mildly humid environments.
Stainless Steel (440C or 304): Provides superior corrosion resistance, making it suitable for marine, medical, or food-processing equipment.
Hybrid Ceramic Bearings: Combine steel rings with silicon nitride (Si3N4) ceramic balls. These bearings reduce friction, withstand higher temperatures, and are ideal for high-speed applications like drones or electric motors.
B. Sealing and Shielding
Open Bearings: No seals, requiring regular lubrication. Used in clean environments where maintenance is feasible.
Shielded (ZZ): Metal shields block dust and debris while retaining grease. Common in industrial machinery.
Sealed (2RS): Rubber seals offer better contamination protection but slightly higher friction. Popular in consumer products like skateboards.

4. Load Capacity and Speed Ratings
Understanding the 608 bearing’s load and speed limits is crucial for optimal performance:
Static Load Rating (C0): Approximately 1.8 kN. This is the maximum load the bearing can withstand without permanent deformation when stationary.
Dynamic Load Rating (C): Around 3.0 kN. Refers to the load the bearing can handle during continuous rotation.
Maximum Speed:
Grease-Lubricated: Up to 15,000 RPM.
Oil-Lubricated: Can exceed 20,000 RPM for hybrid ceramic variants.
Exceeding these limits may lead to premature wear, overheating, or catastrophic failure.
5. Key Applications of 608 Bearings
The 608 bearing’s compact size and reliability make it indispensable in numerous fields:
A. Consumer Products
Skateboards and Rollerblades: Used in wheel hubs to support high-speed rotations and shock loads.
Fidget Spinners and Toys: Provide smooth, quiet operation.
Household Appliances: Found in electric fans, blenders, and hair dryers.
B. Industrial Machinery
Small Motors and Pumps: Ensure efficient power transmission in compact designs.
3D Printers: Critical for precise movement in extruders and linear rails.
Conveyor Systems: Support rollers in lightweight automation setups.
C. High-Tech Applications
Drones and RC Vehicles: Hybrid ceramic 608 bearings reduce weight and enhance motor efficiency.
Medical Devices: Stainless steel variants meet hygiene and corrosion resistance requirements.

6. Selection and Maintenance Tips
A. Choosing the Right 608 Bearing
1. Environment:
- For corrosive settings, opt for stainless steel or ceramic.
- High-temperature applications (e.g., motors) benefit from hybrid bearings.
2. Precision Requirements:
- ABEC-3 is sufficient for most consumer uses.
- ABEC-5 or higher is recommended for CNC machines or optical equipment.
3. Load Type:
- Use angular contact bearings if axial loads dominate.
B. Installation Best Practices
- Avoid hammering bearings directly; use a press or arbor tool.
- Ensure proper alignment between the shaft and housing.
- Follow manufacturer-recommended fits (e.g., shaft tolerance: g6; housing: H7).
C. Maintenance Guidelines
Lubrication: Use high-speed grease (e.g., lithium-based) for shielded bearings. Re-lubricate open bearings periodically.
Inspection: Check for noise, vibration, or discoloration, which indicate wear or contamination.
Replacement: Always replace bearings in pairs to maintain balance.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can a 608 bearing be used in high-speed drones?
Yes, hybrid ceramic 608 bearings are ideal for drone motors due to their low friction and heat resistance.
Q2: How does the 608 differ from the 626 bearing?
The 626 has a 6 mm bore, 19 mm outer diameter, and 6 mm width, making it smaller and less load-capable than the 608.
Q3: Are all 608 bearings waterproof?
No. Only stainless steel or sealed variants offer water resistance. Standard steel bearings will rust if exposed to moisture.
Q4: What causes premature 608 bearing failure?
Common causes include overloading, poor lubrication, misalignment, and contamination.
Conclusion
The 608 bearing’s standardized dimensions (8x22x7 mm), material versatility, and adaptability have cemented its status as a cornerstone of miniature mechanical systems. Whether in everyday gadgets or cutting-edge technology, understanding its specifications and proper usage ensures optimal performance and longevity. By selecting the right variant and adhering to maintenance protocols, engineers and enthusiasts alike can harness the full potential of this ubiquitous component.


