
Image may differ from product. See technical specification for details.
Search for the bearing model you need
Standard
GB,ASTM/AISI,ГОСТ,BS,JIS,NF,DIN / VDEh,DIN / VDEh
Inner ring diameter
10mm-280mm
Outer ring diameter
20mm-400mm
Weight
0.2kg-300kg
Material
GCr15, 52100, 100Cr6, SUJ2, Stainless Steel, German High Nitrogen Stainless Steel CRONIDUR30, Ceramic
Brand
QIBR/OEM/Neutral
Package
QIBR/Standard Industrial Package/OEM
Applications
Machine tool spindle, centrifuge, booster pump, oil pump, blower, various gearboxes, laboratory equipment
Pairing method
DB, DF, DT, DBD, DBB, SU
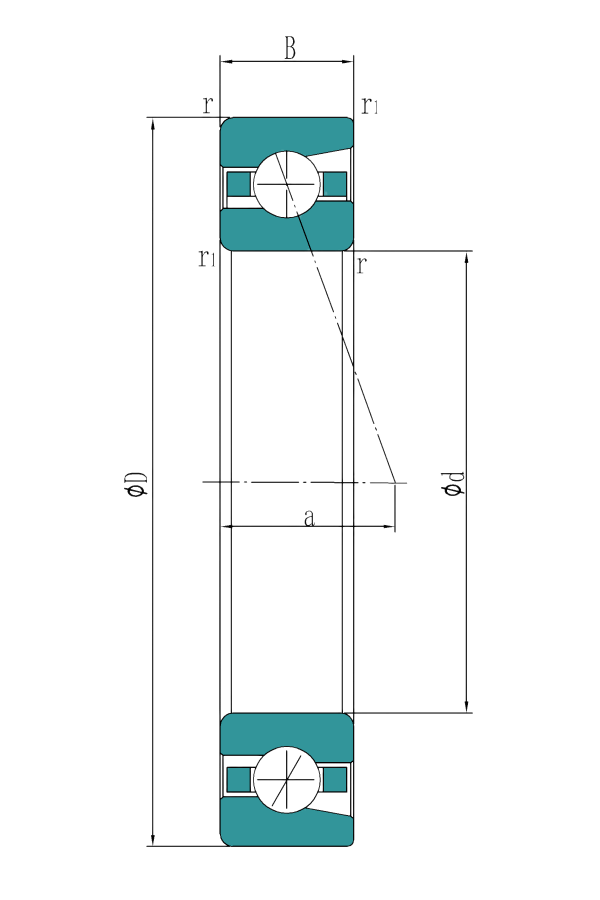
| NO. | Product | Product Number | Inner diameter (d) | Outer diameter (D) | Width (B) | Basic dynamic load rating | Basic static load rating | Mass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 |

|
7202 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 15 mm | 35 mm | 11 mm | 7.41 KN | 3.35 KN | 0.043 kg |
| 202 |

|
7203 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 17 mm | 40 mm | 12 mm | 9.23 KN | 4.15 KN | 0.063 kg |
| 203 |

|
7204 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 20 mm | 47 mm | 14 mm | 11.9 KN | 5.85 KN | 0.1 kg |
| 204 |

|
7205 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 25 mm | 52 mm | 15 mm | 13.5 KN | 7.2 KN | 0.13 kg |
| 205 |

|
7206 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 30 mm | 62 mm | 16 mm | 24.2 KN | 16 KN | 0.2 kg |
| 206 |

|
7207 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 35 mm | 72 mm | 17 mm | 31.9 KN | 21.6 KN | 0.29 kg |
| 207 |

|
7208 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 40 mm | 80 mm | 18 mm | 33.8 KN | 24 KN | 0.33 kg |
| 208 |

|
7209 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 45 mm | 85 mm | 19 mm | 42.3 KN | 31 KN | 0.41 kg |
| 209 |

|
7210 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 50 mm | 90 mm | 20 mm | 44.9 KN | 34 KN | 0.46 kg |
| 210 |

|
7211 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 55 mm | 100 mm | 21 mm | 55.3 KN | 43 KN | 0.61 kg |
| 211 |

|
7212 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 60 mm | 110 mm | 22 mm | 57.2 KN | 46.5 KN | 0.81 kg |
| 212 |

|
7213 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 65 mm | 120 mm | 23 mm | 66.3 KN | 53 KN | 1.05 kg |
| 213 |

|
7214 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 70 mm | 125 mm | 24 mm | 68.9 KN | 58.5 KN | 1.1 kg |
| 214 |

|
7215 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 75 mm | 130 mm | 25 mm | 71.5 KN | 62 KN | 1.2 kg |
| 215 |

|
7216 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 80 mm | 140 mm | 26 mm | 85.2 KN | 75 KN | 1.45 kg |
| 216 |

|
7217 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 85 mm | 150 mm | 28 mm | 99.5 KN | 88 KN | 1.85 kg |
| 217 |

|
7218 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 90 mm | 160 mm | 30 mm | 127 KN | 112 KN | 2.25 kg |
| 218 |

|
7219 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 95 mm | 170 mm | 32 mm | 138 KN | 120 KN | 2.7 kg |
| 219 |

|
7220 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 100 mm | 180 mm | 34 mm | 156 KN | 137 KN | 3.25 kg |
| 220 |

|
7221 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 105 mm | 190 mm | 36 mm | 172 KN | 153 KN | 3.85 kg |
| 221 |

|
7222 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 110 mm | 200 mm | 38 mm | 178 KN | 166 KN | 4.65 kg |
| 222 |

|
7224 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 120 mm | 215 mm | 40 mm | 199 KN | 193 KN | 5.4 kg |
| 223 |

|
7226 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 130 mm | 230 mm | 40 mm | 216 KN | 224 KN | 6.35 kg |
| 224 |

|
7228 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 140 mm | 250 mm | 42 mm | 221 KN | 240 KN | 8.15 kg |
| 225 |

|
727 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 7 mm | 22 mm | 7 mm | 2.96 KN | 1.16 KN | 0.013 kg |
| 226 |

|
728 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 8 mm | 24 mm | 8 mm | 3.71 KN | 1.37 KN | 0.017 kg |
| 227 |

|
729 CDTNHA/P4AL1 | 9 mm | 26 mm | 8 mm | 4.1 KN | 1.66 KN | 0.02 kg |
| 228 |

|
B706-C-P2-U | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 2.36 KN | 0.97 KN | 0.005 kg |
| 229 |

|
B706C | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 2.36 KN | 0.97 KN | 0.005 kg |
| 230 |

|
H719/8AC | 8 mm | 19 mm | 6 mm | 1.6 KN | 0.6 KN | 0.01 kg |
| 231 |

|
H719/8AC/HQ1 | 8 mm | 19 mm | 6 mm | 1.6 KN | 0.6 KN | 0.01 kg |
| 232 |

|
H719/8C | 8 mm | 19 mm | 6 mm | 1.7 KN | 0.7 KN | 0.01 kg |
| 233 |

|
H719/8C/HQ1 | 8 mm | 19 mm | 6 mm | 1.7 KN | 0.7 KN | 0.01 kg |
| 234 |

|
S706CE/P4A | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.56 KN | 0.5 KN | 0.006 kg |
| 235 |

|
S708CE/P4A | 8 mm | 22 mm | 7 mm | 2.34 KN | 0.8 KN | 0.012 kg |
| 236 |

|
S719/8CE/P4A | 8 mm | 19 mm | 6 mm | 1.74 KN | 0.63 KN | 0.007 kg |
| 237 |

|
S719/9CE/P4A | 9 mm | 20 mm | 6 mm | 2.03 KN | 0.8 KN | 0.008 kg |
| 238 |

|
706 ACE/P2 | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.51KN | 0.49 KN | 0.006 kg |
| 239 |

|
706 ACE/P4A | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.51KN | 0.49 KN | 0.006 kg |
| 240 |

|
B706-E-P2-DU | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 2.28 KN | 0.93 KN | 0.005 kg |
| 241 |

|
B706E | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 2.28 KN | 0.93 KN | 0.005 kg |
| 242 |

|
S706 ACD/P4A | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.51KN | 0.49 KN | 0.006 kg |
| 243 |

|
S706 ACE/P4A | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.51KN | 0.49 KN | 0.006 kg |
| 244 |

|
HCB706-C-P2-DB | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.63 KN | 0.67 KN | 0.004 kg |
| 245 |

|
HCB706-CDLR-TX-P2 | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.63 KN | 0.67 KN | 0.004 kg |
| 246 |

|
HCB706C | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.63 KN | 0.67 KN | 0.004 kg |
| 247 |

|
XCB706-CDLR-TX-P2 | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.63 KN | 0.67 KN | 0.004 kg |
| 248 |

|
XCB706-EDLR-TX-P2 | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.63 KN | 0.67 KN | 0.004 kg |
| 249 |

|
H 71914 AC/HQ1 | 70 mm | 100 mm | 16 mm | 19.7 KN | 16.9 KN | 0.28 kg |
| 250 |

|
H 71914 C/HQ1 | 70 mm | 100 mm | 16 mm | 20.9 KN | 17.8 KN | 0.36 kg |
| 251 |

|
H 71915 AC/HQ1 | 75 mm | 105 mm | 16 mm | 21.7 KN | 19.3 KN | 0.30 kg |
| 252 |

|
H 71915 C/HQ1 | 75 mm | 105 mm | 16 mm | 21.7 KN | 19.3 KN | 0.30 kg |
| 253 |

|
H 71918 AC/HQ1 | 90 mm | 125 mm | 18 mm | 25.5 KN | 24.6 KN | 0.46 kg |
| 254 |

|
H 71919 AC/HQ1 | 95 mm | 130 mm | 18 mm | 25.80 KN | 25.40 KN | 0.62 kg |
| 255 |

|
H 71920 AC/HQ1 | 100 mm | 140 mm | 20 mm | 37.90 KN | 35.50 KN | 0.66 kg |
| 256 |

|
H 71921 C/HQ1 | 105 mm | 145 mm | 20 mm | 40.7 KN | 39.1 KN | 0.69 kg |
| 257 |

|
H 71922 AC/HQ1 | 110 mm | 150 mm | 20 mm | 39.0 KN | 38.3 KN | 0.71 kg |
| 258 |

|
H 71924 AC/HQ1 | 120 mm | 165 mm | 22 mm | 40.7 KN | 42.4 KN | 0.97 kg |
| 259 |

|
H 71926 AC/HQ1 | 130 mm | 180 mm | 24 mm | 50.1 KN | 53.4 KN | 1.38 kg |
| 260 |

|
H7024 AC/HQ1 | 120 mm | 180 mm | 28 mm | 54.80 KN | 61.50 KN | 2.1 kg |
| 261 |

|
H7024 C/HQ1 | 120 mm | 180 mm | 28 mm | 58.30 KN | 64.90 KN | 2.1 kg |
| 262 |

|
H7026 AC/HQ1 | 130 mm | 200 mm | 33 mm | 55.10 KN | 63.20 KN | 3.5 kg |
| 263 |

|
H7026 C/HQ1 | 130 mm | 200 mm | 33 mm | 58.60 KN | 66.80 KN | 3.5 kg |
| 264 |

|
H71913 AC/HQ1 | 65 mm | 90 mm | 13 mm | 16.0 KN | 13.7 KN | 0.17 kg |
| 265 |

|
H71913 C/HQ1 | 65 mm | 90 mm | 13 mm | 16.8 KN | 14.5 KN | 0.17 kg |
| 266 |

|
H71916 AC/HQ1 | 80 mm | 110 mm | 16 mm | 21.2 KN | 19.6 KN | 0.31 kg |
| 267 |

|
H71916 C/HQ1 | 80 mm | 110 mm | 16 mm | 22.4 KN | 20.8 KN | 0.31 kg |
| 268 |

|
H71921 AC/HQ1 | 105 mm | 145 mm | 20 mm | 38.4 KN | 36.9 KN | 0.69 kg |
| 269 |

|
HCB706-E-P2-DT | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.63 KN | 0.67 KN | 0.004 kg |
| 270 |

|
HCB706-EDLR-TX-P2 | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.63 KN | 0.67 KN | 0.004 kg |
| 271 |

|
HCB706E | 6 mm | 17 mm | 6 mm | 1.63 KN | 0.67 KN | 0.004 kg |
| 272 |

|
HS7004 AC/HQ1 | 20 mm | 42 mm | 12 mm | 5.80 KN | 4.10 KN | 0.080 kg |
| 273 |

|
HS7004 C/HQ1 | 20 mm | 42 mm | 12 mm | 6.1 KN | 4.3 KN | 0.080 kg |
| 274 |

|
HS7004AC | 20 mm | 42 mm | 12 mm | 5.80 KN | 4.10 KN | 0.080 kg |
| 275 |

|
HS7006 AC/HQ1 | 30 mm | 55 mm | 13 mm | 8.10 KN | 6.30 KN | 0.130 kg |
| 276 |

|
HS7006AC | 30 mm | 55 mm | 13 mm | 8.10 KN | 6.30 KN | 0.130 kg |
| 277 |

|
HS7007 AC/HQ1 | 35 mm | 62 mm | 14 mm | 8.70 KN | 7.40 KN | 0.180 kg |
| 278 |

|
HS7007AC | 35 mm | 62 mm | 14 mm | 8.70 KN | 7.40 KN | 0.180 kg |
| 279 |

|
HS7008 AC/HQ1 | 40 mm | 68 mm | 15 mm | 9.30 KN | 8.40 KN | 0.20 kg |
| 280 |

|
HS7008AC | 40 mm | 68 mm | 15 mm | 9.30 KN | 8.40 KN | 0.22 kg |
| 281 |

|
HS7009 AC/HQ1 | 45 mm | 75 mm | 16 mm | 11.80 KN | 10.70 KN | 0.26 kg |
| 282 |

|
HS7009AC | 45 mm | 75 mm | 16 mm | 11.80 KN | 10.70 KN | 0.28 kg |
| 283 |

|
HS7010 AC/HQ1 | 50 mm | 80 mm | 16 mm | 12.20 KN | 11.70 KN | 0.28 kg |
| 284 |

|
HS7010AC | 50 mm | 80 mm | 16 mm | 12.20 KN | 11.70 KN | 0.30 kg |
| 285 |

|
HS7011 AC/HQ1 | 55 mm | 90 mm | 18 mm | 17.50 KN | 16.80 KN | 0.41 kg |
| 286 |

|
HS7011AC | 55 mm | 90 mm | 18 mm | 17.50 KN | 16.80 KN | 0.44 kg |
| 287 |

|
HS7012 AC/HQ1 | 60 mm | 95 mm | 18 mm | 18.20 KN | 18.20 KN | 0.43 kg |
| 288 |

|
HS7012AC | 60 mm | 95 mm | 18 mm | 18.20 KN | 18.20 KN | 0.47 kg |
| 289 |

|
HS7013 AC/HQ1 | 65 mm | 100 mm | 18 mm | 18.80 KN | 19.70 KN | 0.46 kg |
| 290 |

|
HS7013AC | 65 mm | 100 mm | 18 mm | 18.80 KN | 19.70 KN | 0.50 kg |
| 291 |

|
HS7014 AC/HQ1 | 70 mm | 110 mm | 20 mm | 24.40 KN | 25.2 KN | 0.64 kg |
| 292 |

|
HS7014AC | 70 mm | 110 mm | 20 mm | 24.40 KN | 25.2 KN | 0.69 kg |
| 293 |

|
HS7015 AC/HQ1 | 75 mm | 115 mm | 20 mm | 24.70 KN | 26.30 KN | 0.67 kg |
| 294 |

|
HS7015AC | 75 mm | 115 mm | 20 mm | 24.70 KN | 26.30 KN | 0.73 kg |
| 295 |

|
HS7016AC | 80 mm | 125 mm | 22 mm | 29.50 KN | 31.70 KN | 0.99 kg |
| 296 |

|
HS7017AC | 85 mm | 130 mm | 22 mm | 29.90 KN | 32.90 KN | 1.03 kg |
| 297 |

|
HS7018AC | 90 mm | 140 mm | 24 mm | 35.10 KN | 39.10 KN | 1.35 kg |
| 298 |

|
HS7019AC | 95 mm | 145 mm | 24 mm | 35.50 KN | 40.60 KN | 1.40 kg |
| 299 |

|
HS7020AC | 100 mm | 150 mm | 24 mm | 36.00 KN | 42.10 KN | 1.46 kg |
| 300 |

|
HS7021 AC/HQ1 | 105 mm | 160 mm | 26 mm | 46.40 KN | 53.20 KN | 1.8 kg |


