Product solution for stepper motor bearing seizure caused by different materials at high and low temperatures
- Industry
- Building Water Supply System Industry
- Location
- Germany
- Goals
- The application of QIBR precision angular contact ball bearings optimized the precision and stability of CNC machines, improving processing efficiency and quality, reducing energy consumption and failure rates, enhancing the quality of the machined surfaces, and lowering maintenance costs and downtime. This brought numerous benefits to the development and application of CNC machines.
Products used
Product solution for stepper motor bearing seizure caused by different materials at high and low temperatures
- Under high temperatures of 95°c and low temperatures of -60°c, a simulation analysis was conducted on stepper motors made from differentmaterials. The simulation results revealed the primary cause of bearing sticking issues in stepper motors due to material diferences at extremetemperatures. lmprovement measures were proposed and their feasibility was verified through experiments.
a). Challenges
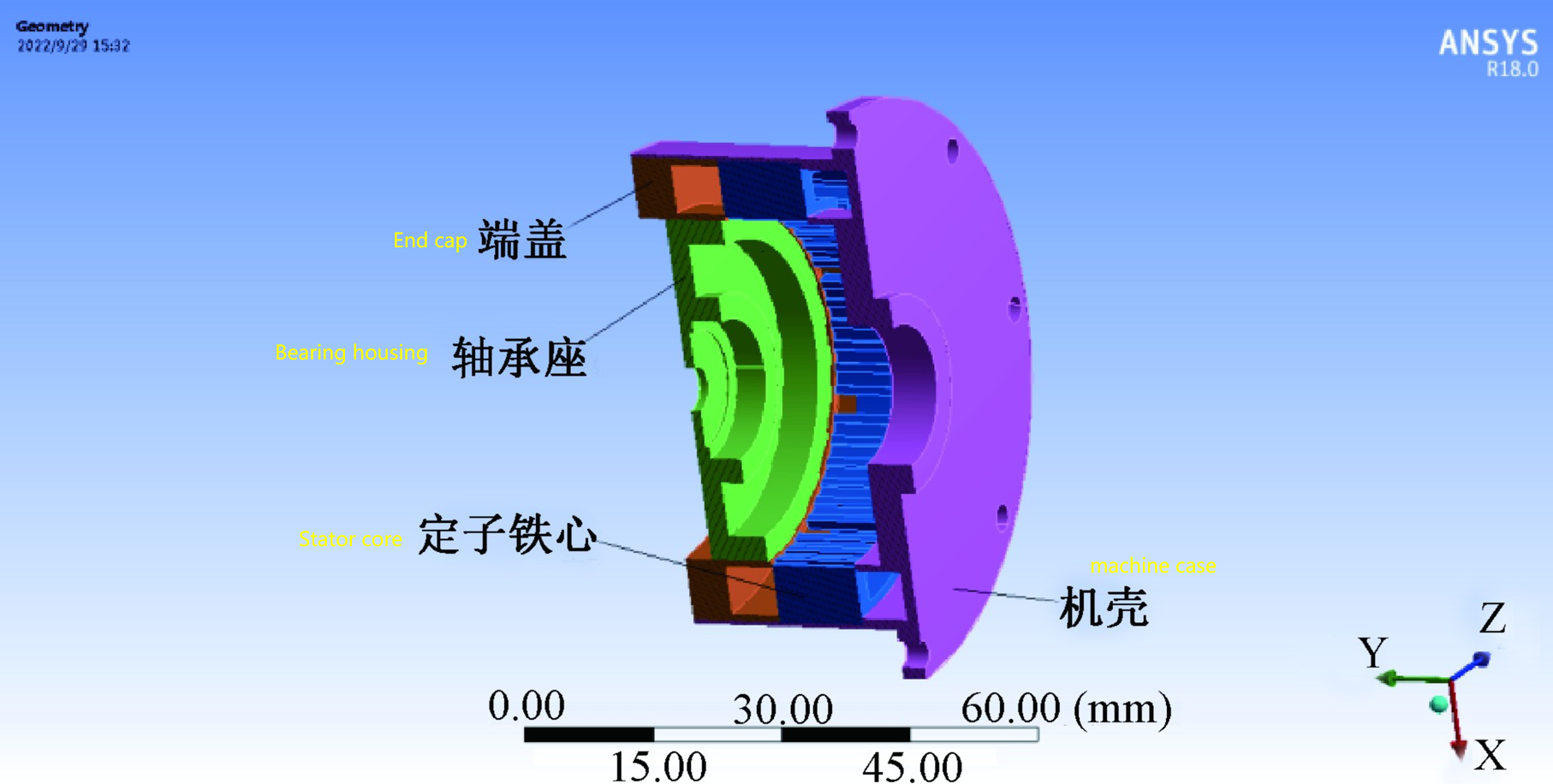
Steper motors are actuators that convert electrical puise signals into anqular displacement. They have a simple and convenientsystem with low cost,making them widely used in openloop positioning systems that require higher resolution. With the advancement of modem science and technology,there are increasing demands for stepper motors to have higreliabllty. ow anerov consumption. and iohtweioht desians,.To meetthe reourements for iohtweioht desion.the housing and and caos of steoer motors are often made frowlightweight materials ike hard aluminum aloys instead of structural stel, whie stil meeting structural strength requirements to reduce the overallweight of the motor
b) Solution (How QIBR solves the problem)
QlBR techicians used the finie element anawsis sofware ANsYs Workbench to pertom simulation analysis on steper motors with housings and end caps made from diferenmaterials at hioh temperatures of95*c and low temperalures of -60"c, They analvzed the main reasons for anguar contact ball bearing iammin isues in steaper motors caused bvmaterial differences under these temperature conditions and proposed improvement measures
c) Result
· Finite element simulation analysis was conducted on steper motors with housings and end caps made of hard aluminum aloy and structural stelat high temperatures of 95℃ andlow temperatures of -60℃. The contour maps of axial displacement and radial displacement at the stator bearing position are shownin figures 2 to 5, respectively.
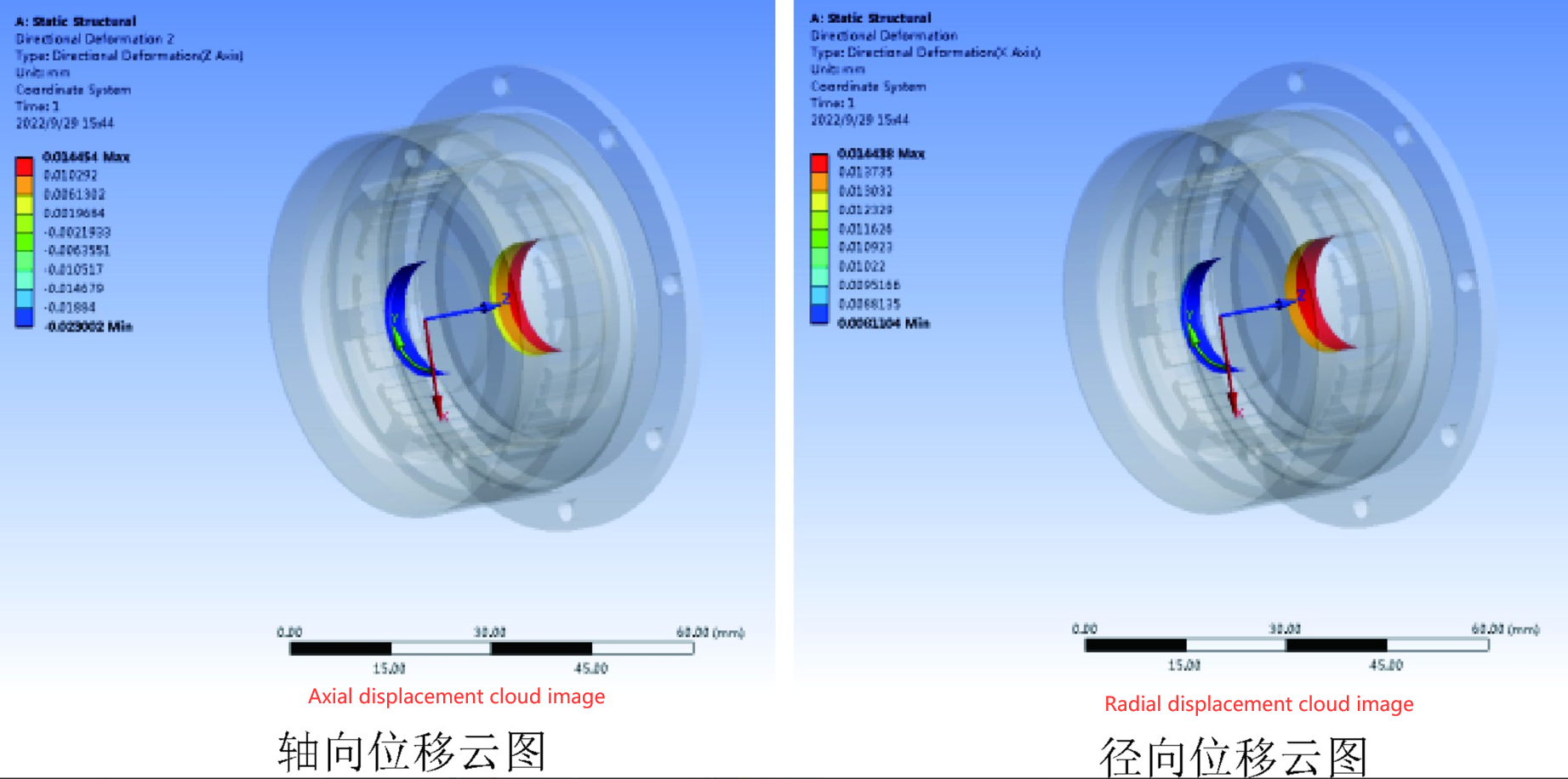
Picture 1: Displacement cloud diagram of bearing stop when the housing end cover is made of aluminum alloy at 295℃
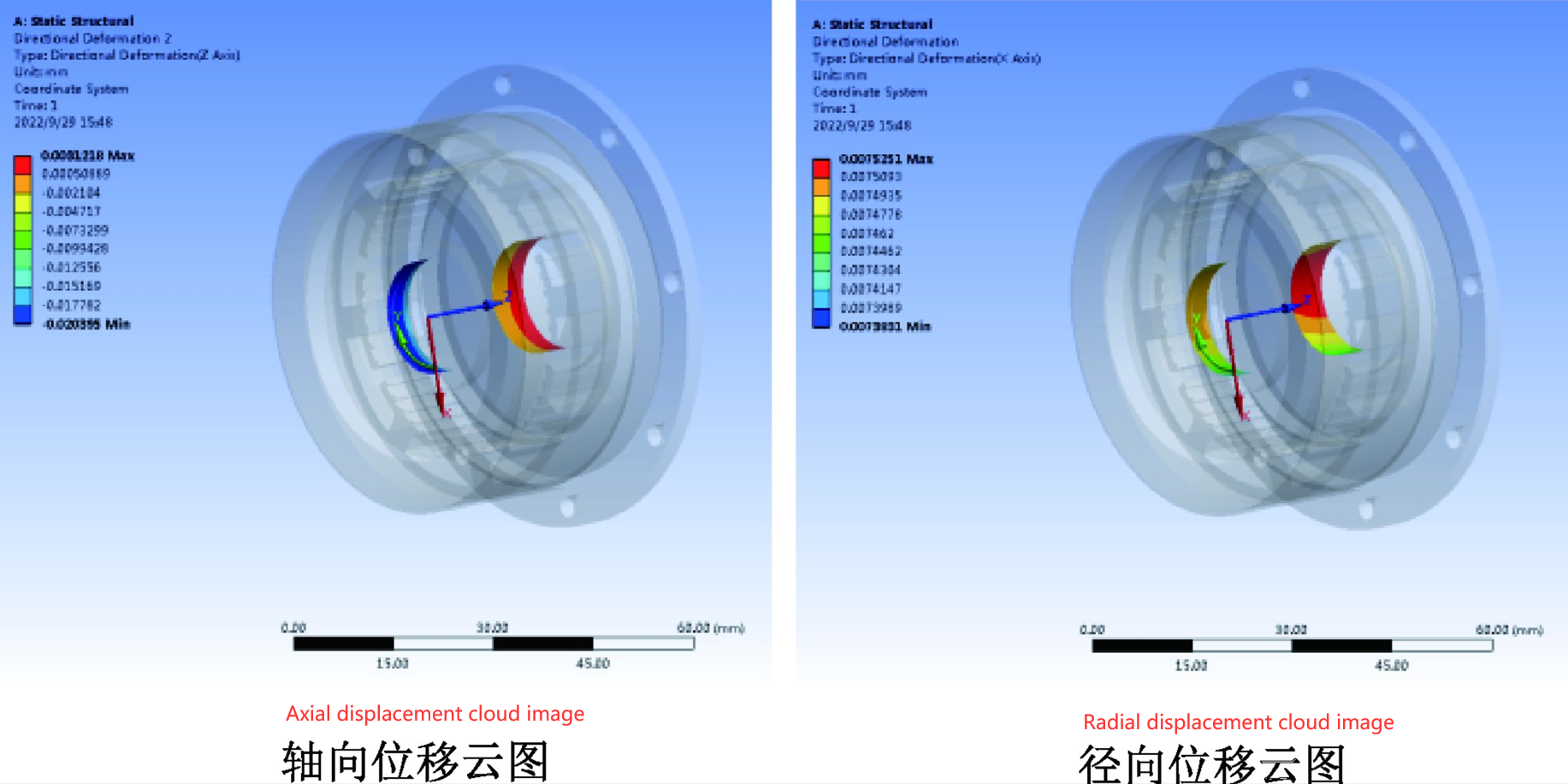
Picture 2: Displacement cloud diagram of bearing stop when the housing end cover is made of structural steel at 395℃
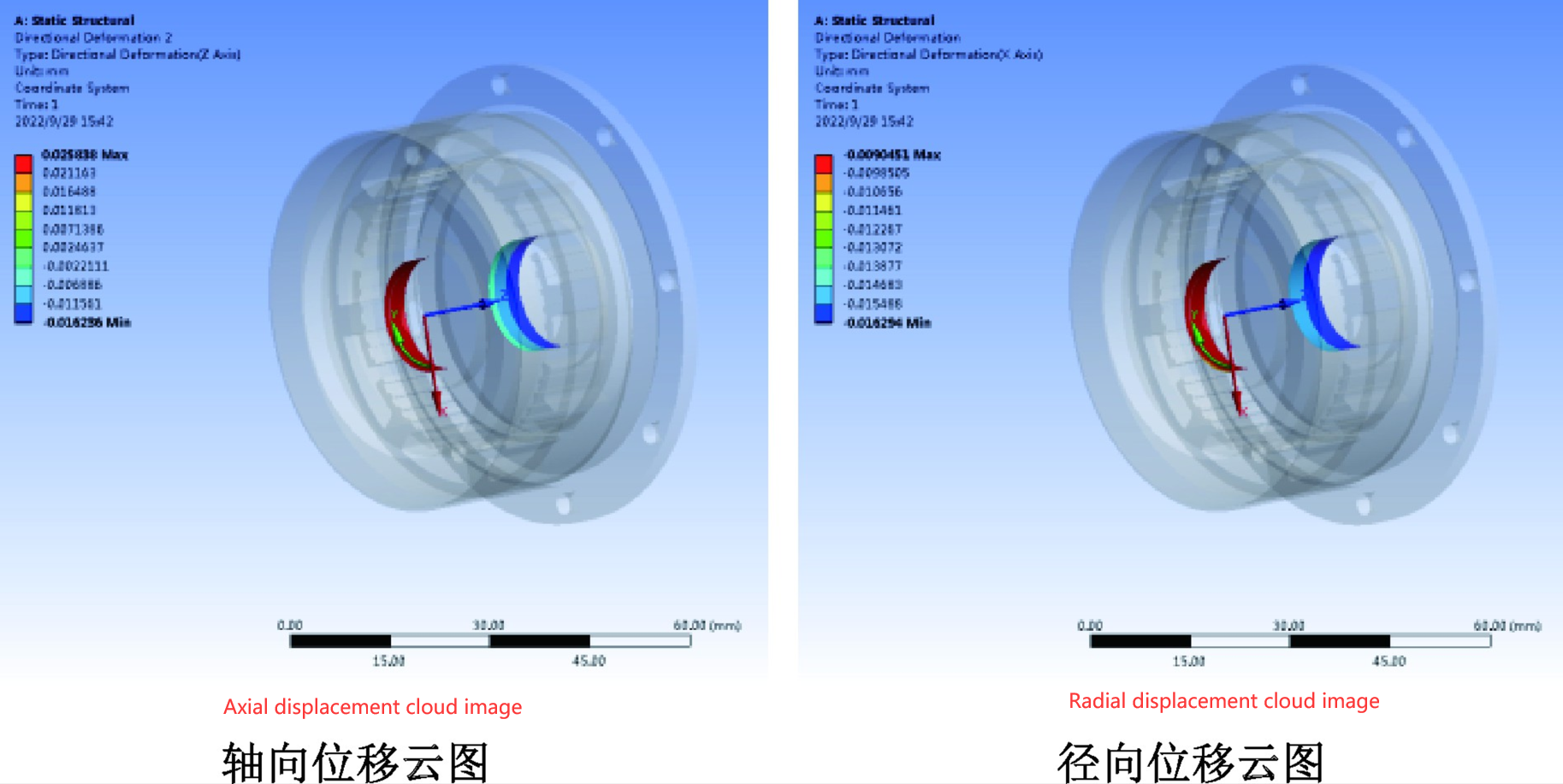
Picture 3: Displacement cloud diagram of bearing stop when the housing end cover is made of aluminum alloy at 60℃
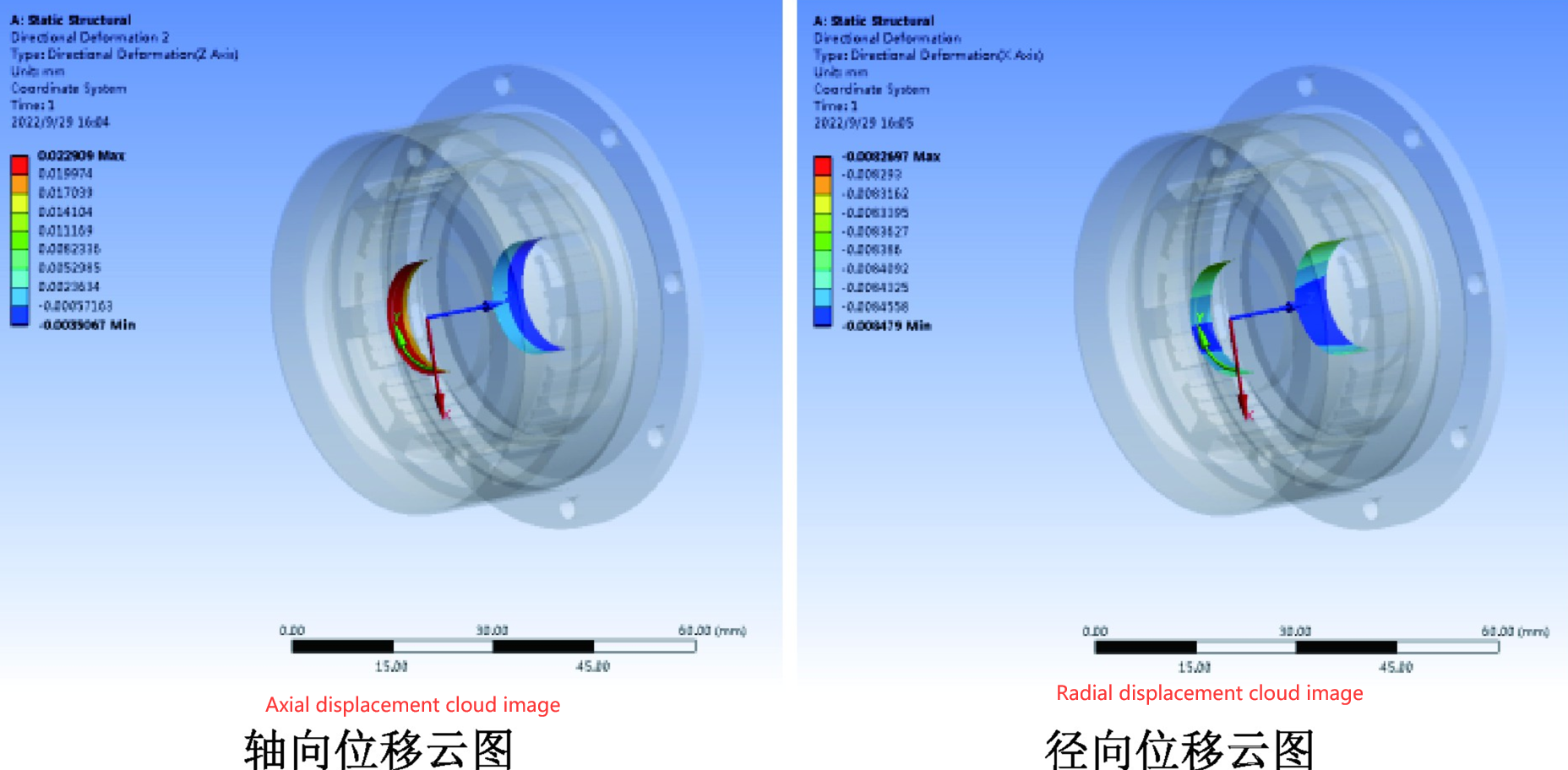
Picture 4: Displacement cloud diagram of bearing stop when the housing end cover is made of structural steel at 60℃
At high temperatures of 95℃and low temperatwres of -60℃,when the housing and end caps are made of hard alumimnum aloy and strncturalstel, the maximum axial displacement andmaximum radial displacement at the stator bearing position are shown in Table 1.
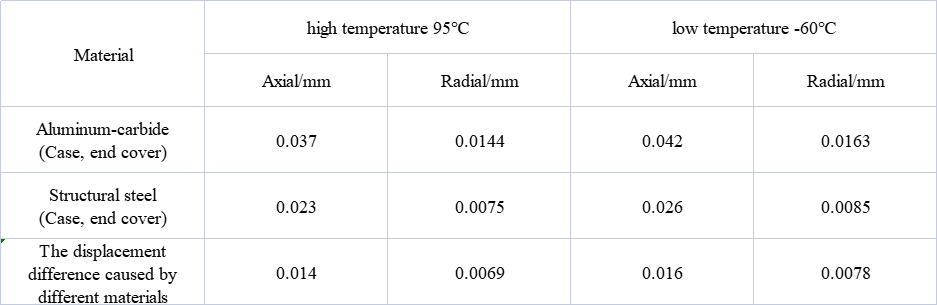
Under high and low temperatures, the use of different materials for the housing and end caps (primarily due to the different thermal expansion coefficients—hard aluminum alloy has a thermal expansion coefficient of 2.3 × 10⁻⁵ K⁻¹, while structural steel has a thermal expansion coefficient of 12 × 10⁻⁵ K⁻¹) causes differences in the axial and radial displacements at the bearing position. At high temperature (95°C), the displacement differences at the bearing position are 0.014 mm for axial displacement and 0.069 mm for radial displacement. At low temperature (-60°C), the displacement differences are 0.016 mm for axial displacement and 0.0078 mm for radial displacement.
When the housing and end caps are made of hard aluminum alloy under these temperature conditions, the differences in axial and radial displacements at the bearing position directly affect the outer diameter of the bearings at both ends, thereby reducing the axial and radial play of the bearings and ultimately causing bearing jamming issues. To address this, the paper proposes increasing the fit clearance between the stator bearing position and the bearings, as well as the axial clearance between the stator and rotor of the stepper motor, by 0.008 mm and 0.017 mm, respectively, to compensate for material variations and prevent bearing jamming.
The QIBR engineering team assisted the customer by disassembling a faulty motor, cleaning the stator and rotor with acetone, and then machining the inner bore of the stator bearing position by 0.008 mm. They also machined the end faces of the bearing positions at both ends of the shaft by 0.017 mm. After reassembling the stator and rotor, they conducted electrical testing at temperatures of 95°C and -60°C using experimental equipment. The tests showed that the shaft rotated freely and smoothly without any jamming issues.
· Reduced energy consumption and failure rates: The excellent design and manufacturing process of precision anguar contact ball bearing reduce energy consumption and increase the bearing’s lifespan and reliability. This helps lower the energy consumption of NC machines and reduces downtime and maintenance costs caused by bearing failures.
· The issue of bearing seizure in stepper motors caused by material differences under high and low temperatures was addressed by implementing improvement measures. Specifically, the fit clearance between the stator bearing block and the bearing was increased by 0.008 mm, and the axial clearance between the stator and rotor of the stepper motor was increased by 0.017 mm. These adjustments were made to counteract the axial and radial displacement differences caused by the varying materials.
· It was discovered that the primary cause of bearing seizure in stepper motors under high and low temperatures due to material differences is as follows: The use of different materials for the housing and end caps (mainly due to differences in thermal expansion coefficients) results in axial and radial displacement differences in the bearing block. This displacement difference directly affects the outer diameter of the bearings at both ends, reducing or even eliminating the axial and radial clearances of the bearings, ultimately leading to bearing seizure.
Customer Testimonials
QIBR provided us with a specialized solution by recommending precision anguar contact ball bearing to replace standard ball bearings. They offered professional advice and optimization strategies to address the issue of low product precision in our equipment during operation. These suggestions and improvements not only helped us enhance product quality and performance but also brought a range of significant benefits: increased production value, reduced costs, minimized downtime, improved product quality, and optimized operational processes.
Through our collaboration with QIBR, we not only resolved the current challenges and issues but also laid a solid foundation for future development, achieving sustained business growth and sustainable development.
QIBR provided us with a specialized solution by recommending precision angular contact ball bearings to replace standard ball bearings.