Newsroom
Diagnosis and Analysis of Poor Bearing Lubrication
2019-01-23Poor lubrication is a major cause of cylindrical roller bearing failure, accounting for more than one-third of all cases. During cylindrical roller bearing operation, improper lubrication is a common issue that many engineers face. This article introduces the knowledge related to diagnosing and analyzing bearing problems caused by poor lubrication.
1. Mechanism of Poor Bearing Lubrication
Lubrication primarily reduces friction in bearings. Typically, lubricants work by forming an oil film between two moving surfaces, separating the friction pairs and thereby reducing friction. In the case of cylindrical roller bearing, the oil film separates the rolling elements from the raceway. If the lubricant completely separates the rolling elements from the raceway, this is referred to as a state of hydrodynamic lubrication, which is an ideal lubrication condition. The essence of poor lubrication is that the oil film fails to separate the rolling elements and the raceway, resulting in direct metal-to-metal contact, accelerating cylindrical roller bearing failure.
2. Symptoms of Poor Bearing Lubrication
As mentioned above, the essence of poor lubrication is that the oil film does not completely separate the rolling elements from the raceway, leading to direct contact between the rolling elements and the raceway. This results in metal-to-metal contact within the cylindrical roller bearing during operation.
In a well-lubricated state, there is no direct metal contact inside the bearing, and the overall friction is minimal, generating very little heat. Under poor lubrication conditions, the oil film breaks down, leading to metal-to-metal contact, increasing friction, and generating more heat during bearing operation. This results in the bearing running at higher temperatures, commonly referred to as bearing overheating.
Other bearing failures can also lead to increased temperature and overheating. So, how can you differentiate between temperature increases caused by poor lubrication and other failure modes?
In cases of pure poor lubrication, the root cause is the lubricant’s inadequate basic properties, mainly related to viscosity. When poor lubrication initially occurs, there are no other issues with the bearing, so only the rolling element and raceway surface experience abnormal friction, with no significant damage to the bearing surface in the short term. The friction intensifies, and the temperature rises. In this case, you can observe an increase in bearing temperature, but since all bearing components are in good condition, there are no abnormalities in the vibration levels at their characteristic frequencies. Field observations will show rising bearing temperatures, but no changes in vibration or other status indicators.
3. Failure Analysis of Poor Bearing Lubrication
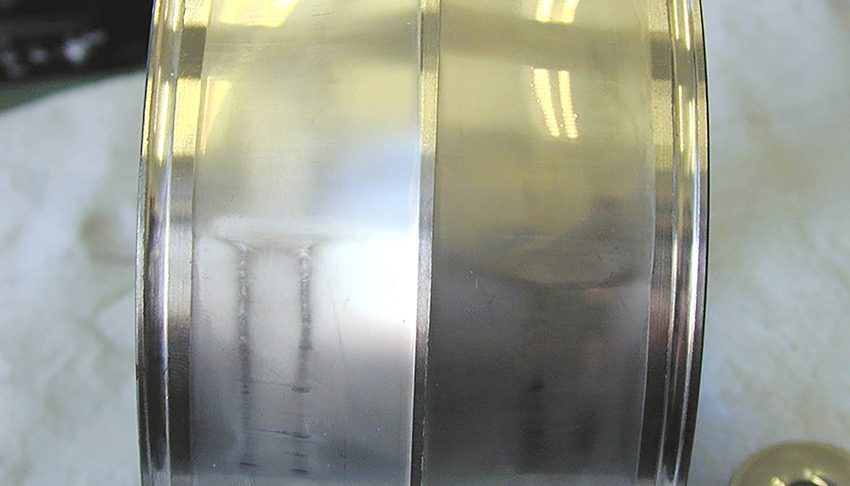
When poor lubrication occurs, the rolling elements and the raceway come into direct metal contact, which can lead to surface-originated fatigue or surface degradation. As shown in the following image, the surface roughness of the raceway changes, and the bearing begins to exhibit surface degradation. If it’s purely a lubrication issue (excluding contamination), the metal surface may develop surface-originated fatigue, initially appearing as uneven, mirror-like areas, eventually leading to surface spalling.
4. Addressing Poor Bearing Lubrication
As previously mentioned, poor lubrication is mainly caused by the lubricant's viscosity being inadequate to form the necessary oil film. In such cases, the factors affecting lubrication viscosity must be adjusted accordingly.
If poor lubrication occurs during the initial manufacturing stage, it may be related to improper lubricant selection. When lubrication issues arise, check the lubricant selection, filling process, and ensure the correct lubricant and amount are used in the equipment.
In cases where the equipment was originally in good condition but suddenly exhibits poor lubrication signs during operation, it is necessary to investigate factors that may have influenced lubrication during this time. These may include temperature fluctuations, lubricant replenishment, contamination entry, or mixing of different greases, among others.
If poor lubrication symptoms are identified and corrected in the early stages, premature cylindrical roller bearing failure can be avoided. In such cases, the cylindrical roller bearing may not yet be damaged, and correcting the lubrication problem will resolve all failure symptoms.


