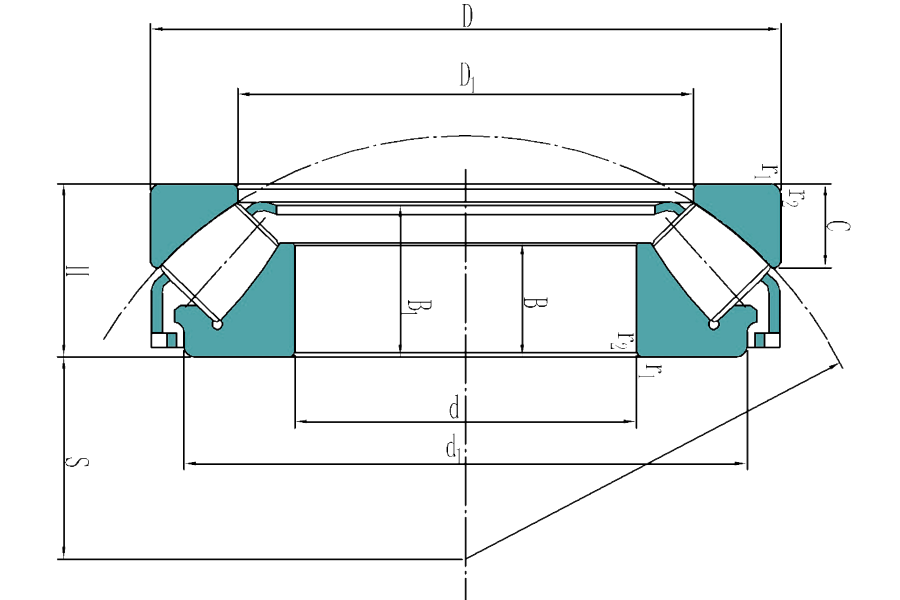
29424 E
- Inner diameter:
- 120 mm
- Outer diameter:
- 250 mm
- Width:
- 78 mm
- Mass:
- 17.5 kg
We will provide you with the most suitable solution.
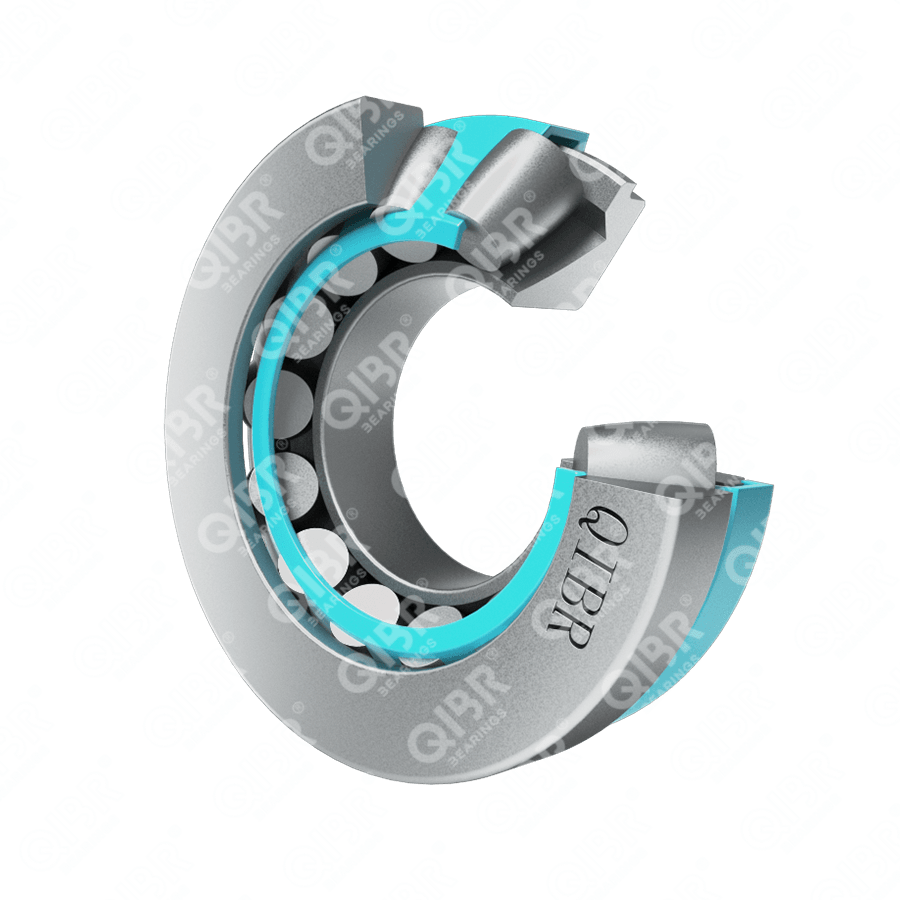

Image may differ from product. See technical specification for details.
Specifications
Seris - 29424 E
Description
QIBR - 29424 E Thrust Roller Bearing Advantages and Applications
29424 E Thrust Roller Bearing, high axial load capacity, high rigidity, Bore is 120 mm, Outer diameter (D) is 250 mm, Height (H) is 78 mm, Mass is 17.5 kg, suitable for wind turbines, mixers, reactors and flight control systems, etc., and is the most widely used bearing in working conditions with high performance requirements.
QIBR - 29424 E Thrust Roller Bearing Characteristics
29424 E Thrust Roller Bearing, long life, strong adaptability. 29424 E Thrust Roller Bearing, can withstand unidirectional or bidirectional axial loads and a certain overturning moment, suitable for mechanical equipment with high durability requirements.
29424 E Thrust Roller Bearings Features and Advantages
Allowable Misalignment Error: Thrust roller bearings possess self-aligning capabilities, allowing them to tolerate misalignment errors.
Load Capacity: The excellent fit between the rollers and the raceway enables the bearing to support heavy axial loads while also accommodating some radial loads.
High-Speed Capability: The cage design and the good fit between the rollers and the raceway make these bearings suitable for relatively high speeds.
Low Friction: By optimizing the contact at the roller end faces, friction heat generation is kept at a low level during high-speed operation.
Long Service Life: The special roller profile reduces edge stresses at the contact points between the rollers and the raceway.
Application: Thrust roller bearings are widely used in machine tools, aerospace, metallurgy and mining, heavy machinery, automotive industry, agricultural machinery, and power equipment.
QIBR - 29424 E Thrust Roller Bearings Optimization
High-Performance Materials: Suitable materials can be selected based on customer requirements, such as 52100, 100Cr6, SUJ2, etc.
Cage Selection: Customers can choose from various cage materials based on their application needs, including machined brass cages, stamped steel window cages, and machined copper cages.
Grease Selection: Lubricants can be chosen according to the operational requirements of the bearings, such as SKF LGET 2 or Shell Gadus S5 V142W 00.
Further Customization: QIBR can design and optimize thrust ball bearings according to customer usage conditions and requirements.
QIBR - 29424 E Thrust Roller Bearings Quality Control
Dimension measurement: Various high-precision instruments are used to measure multiple dimensions of the bearings, achieving a maximum precision of 0.001mm.
Rotation accuracy: Small surface defects or deviations are measured with a micrometer, with a measurement precision of up to 0.001mm.
Hardness measurement: Surface hardness is measured using a hardness tester, with precision up to ±0.5HRC.
Metallographic analysis: The internal metallographic structure of metals is analyzed using a professional metallographic microscope.
Geometric tolerance: The geometry and relative position of the bearing are measured using a profile projector.
Noise monitoring: Vibration during operation is monitored with a vibration meter to obtain noise data.
Raw material control: Steel and parts are sourced from ISO 14001-certified suppliers, ensuring product stability while promoting sustainable development.
Features & Benefits
Thrust roller bearings sustain only axial loads.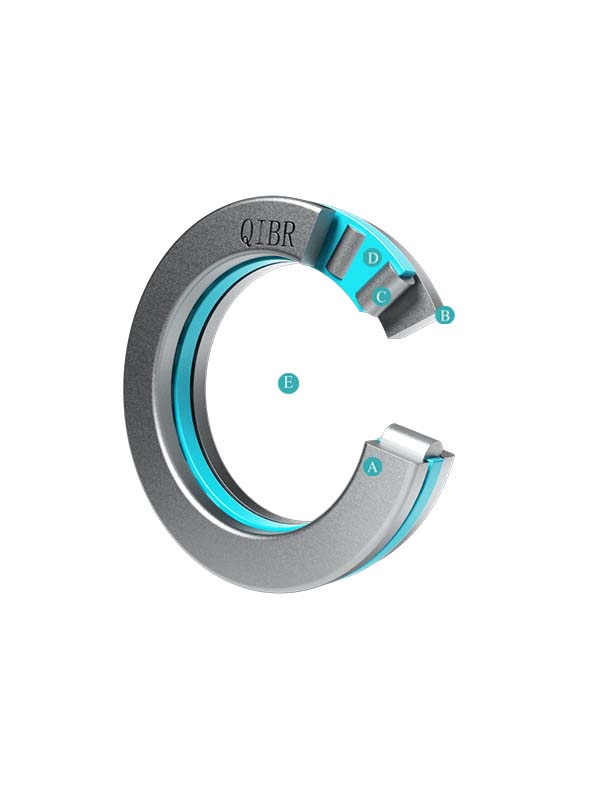
Downloads