Newsroom
Ball Bearing Disassembly Methods
2017-07-02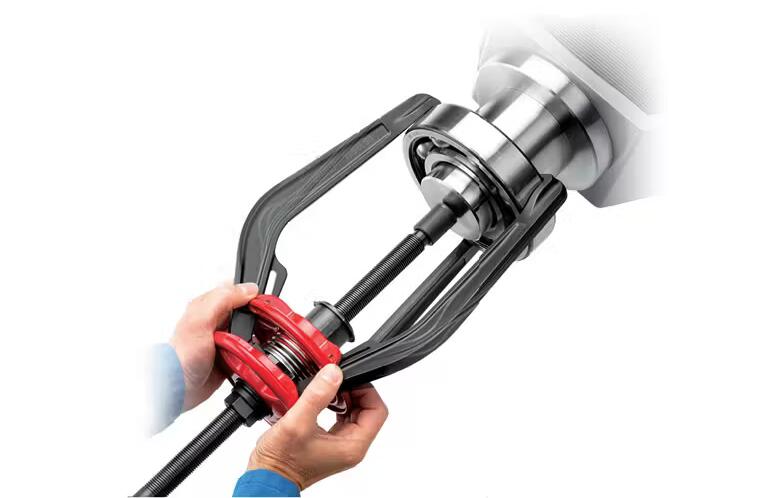 
I. Pre-Disassembly Preparations
1. Safety First
- Wear protective gloves and safety goggles
- Ensure proper ventilation in the work area
2. Workspace Organization
- Maintain a clean and organized disassembly environment
- Clear obstacles from the work area
3. Tool Preparation
- Select appropriate disassembly tools based on bearing type and installation method
- Prepare auxiliary materials (penetrating oil, cleaning agents, etc.)
4. Position Marking
- Record the original position and orientation (especially for angular contact bearings)
- Use marking paint or tags for identification
II. Common Disassembly Methods
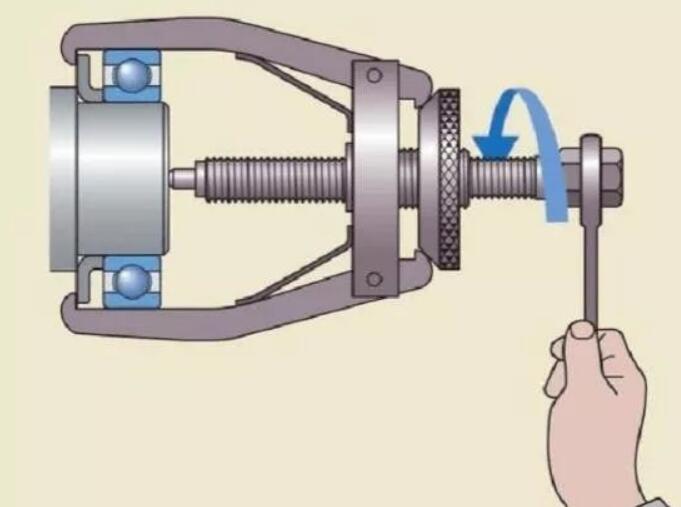
1. Mechanical Puller Method
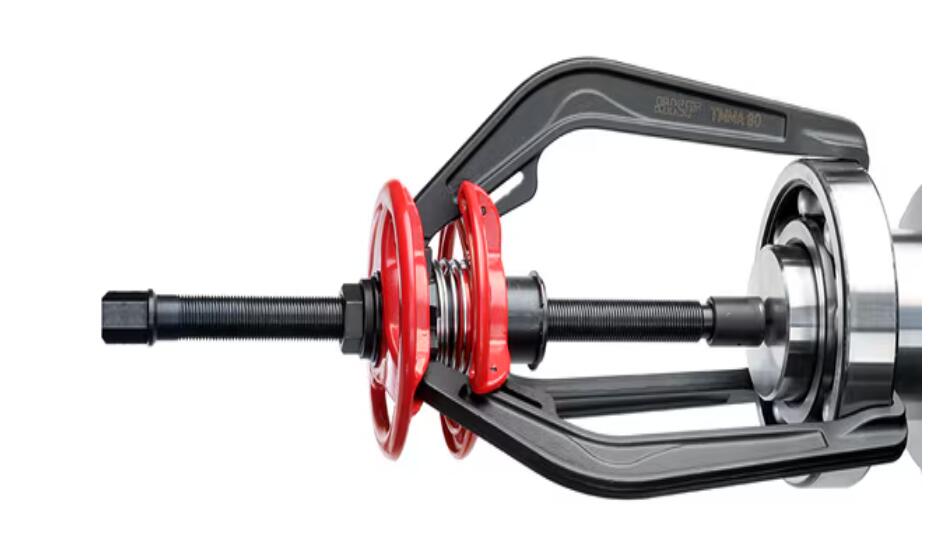

Applications: Small shaft diameters with light interference fits
Tools:
- Two-jaw or three-jaw bearing pullers
- Hydraulic pullers (for larger bearings)
Procedure:
- Securely attach puller jaws to the ball bearing inner ring
- Align puller center with shaft axis
- Apply steady, even pulling force
- For stubborn bearings: Apply controlled heat to inner ring (≤120°C)
Precautions:
- Never grip the outer ring - risk of ball bearing damage
- Use penetrating oil for tight fits
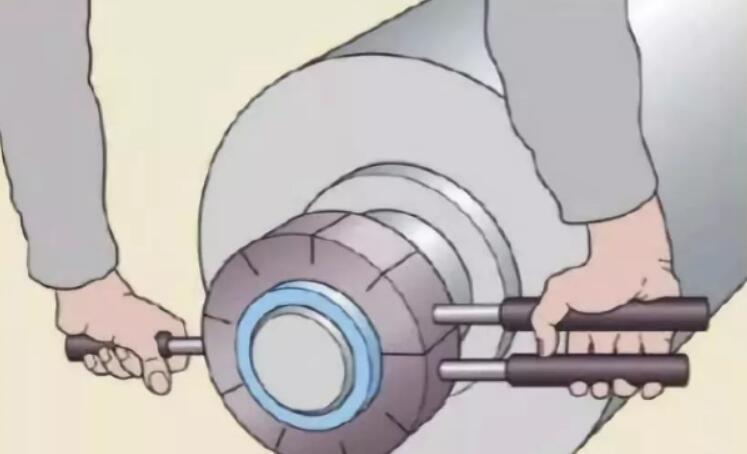
2. Hydraulic Disassembly Method
Applications: Large ball bearings or heavy interference fits
Equipment:
- Hydraulic pump system
- Specialized disassembly sleeves
Advantages:
- Even force distribution
- Minimized shaft/bearing damage
3. Thermal Disassembly Method
Principle: Utilize thermal expansion/contraction
Procedure:
1. Heat inner ring with induction heater or heat gun (80-120°C range)
2. Quickly remove with puller
Prohibited:
Direct flame heating (causes material annealing)
4. Impact Method (Last Resort)
Applications: Non-critical small bearings only
Proper Technique:
- Use copper or soft metal drifts
- Apply even impacts to inner ring
- Never strike outer ring or rolling elements
III. Special Case Handling
1. Rusted/Seized Bearings:
- Pre-treat with penetrating oil (e.g., WD-40)
- Allow several hours for penetration
- Combine with thermal method
2. Plastic Cage Bearings:
- Temperature limit: 80°C max
- Prefer mechanical puller methods
3. Miniature Bearings:
- Use precision micro-pullers
- Exercise extreme care
IV. Post-Disassembly Inspection
1. Component Examination:
- Check shaft and housing for wear
- Assess bearing failure patterns (for predictive maintenance)
2. Surface Preparation:
- Clean mating surfaces
- Remove burrs and residues
V. Common Mistakes and Prevention
Error Consequence Correct Practice
Striking outer ring Damages rolling elements/cage Always apply force to inner ring
Improper puller selection Tool slippage/injury Use size-matched professional tools
Excessive heating Material annealing Monitor with thermometer (stay within limits)
VI. Professional Recommendations
1. Expert Consultation: Recommended for precision/valuable equipment
2. Documentation: Preserve manufacturer's disassembly instructions
3. Design Considerations: Incorporate disassembly accessibility during design phase
4. Maintenance Benefits: Regular maintenance significantly reduces disassembly difficulty
Mastering these professionalball bearing disassembly techniques will improve work efficiency, minimize potential equipment damage and extend machinery service life.
For more info, feel free to contact QIBR.


