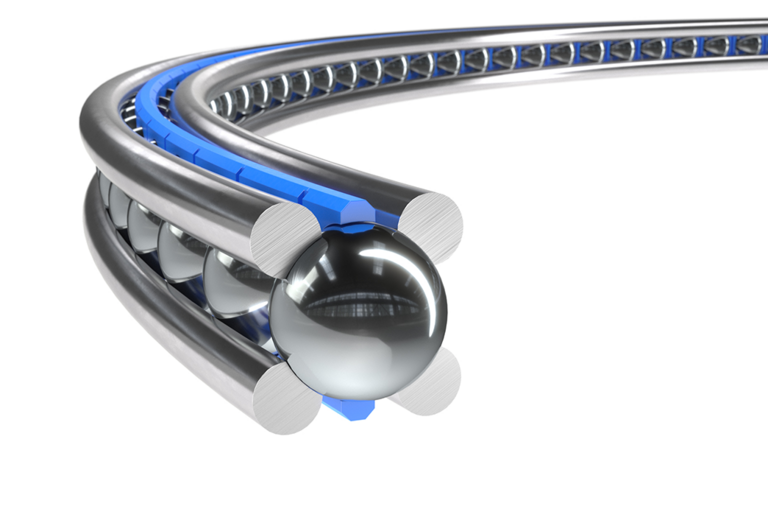
A wire race bearing is a specialized type of rolling-element bearing designed to handle high loads, misalignment, and harsh operating conditions while maintaining compact dimensions. Unlike traditional bearings that use solid raceways (e.g., inner and outer rings made of metal), wire race bearings replace these solid rings with high-strength, precision-formed steel wires as the raceways for rolling elements (typically balls or rollers). 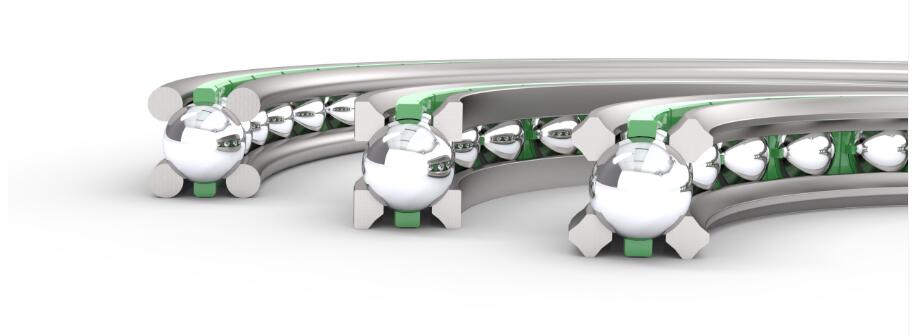
Key Components of a Wire Race Bearing
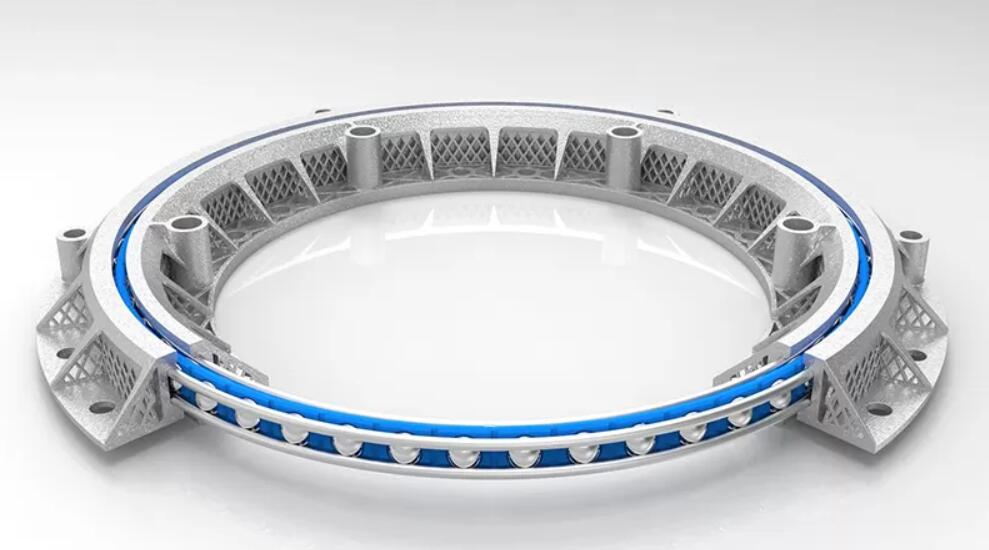
Wire race bearings consist of three core components:
- Wire Raceways: High-carbon or alloy steel wires (often hardened and ground) that form the inner and outer race surfaces. These wires are shaped into circular or linear profiles to guide the rolling elements.
- Rolling Elements: Balls, cylindrical rollers, or spherical rollers that roll between the wire raceways, reducing friction between moving parts.
- Cage/Retainer: A structure (usually made of metal, plastic, or composite) that separates and guides the rolling elements to prevent contact and ensure uniform load distribution.

How Wire Race Bearings Work
The wire raceways act as the contact surfaces for the rolling elements. When a load is applied, the rolling elements distribute the load evenly across the wires, which deform slightly under pressure to absorb stress. This flexibility allows the bearing to accommodate misalignment (angular or parallel) and shaft deflection more effectively than rigid solid-race bearings.
Advantages of Wire Race Bearings
- Compact Design: Eliminating solid rings reduces overall size and weight, making them ideal for applications with limited space.
- High Load Capacity: The wire raceways distribute loads evenly, enabling the bearing to handle radial, axial, and combined loads effectively.
- Misalignment Tolerance: The flexible wire raceways allow for small angular or parallel misalignments between the shaft and housing, reducing stress on components.
- Corrosion Resistance: With proper material selection (e.g., stainless steel wires), wire race bearings can resist corrosion in harsh environments.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to large solid-race bearings, wire race bearings are often more affordable due to lower material and manufacturing costs.
Applications
Wire race bearings are used in a wide range of industries where compactness, high load capacity, and misalignment tolerance are critical:
- Robotics: Joints and arms of industrial robots, where precision and space efficiency are essential.
- Machine Tools: Spindles, linear guides, and rotary tables, where high loads and accuracy are required.
- Aerospace: Actuators, landing gear components, and satellite mechanisms, where lightweight and reliable performance is key.
- Medical Equipment: Imaging machines (e.g., CT scanners) and surgical robots, where smooth motion and compact design are necessary.
- Material Handling: Conveyors, lift systems, and robotic grippers, where durability and load capacity matter.
Types of Wire Race Bearings
Wire race bearings are categorized based on their design and motion type:
- Radial Wire Race Bearings: Designed to handle primarily radial loads, with wire raceways arranged concentrically around the shaft.
- Axial Wire Race Bearings: Optimized for axial loads, with wire raceways positioned parallel to the bearing’s face.
- Angular Contact Wire Race Bearings: Handle combined radial and axial loads, with raceways angled to transmit forces efficiently.
- Linear Wire Race Bearings: Used for linear motion applications, with wires guiding rolling elements along a track.