Newsroom
Where is the R188 bearing used?
2024-10-27The R188 bearing belongs to the category of miniature bearings. It has an inner diameter of 8mm, an outer diameter of 19mm, and a width of 5mm. Despite its seemingly thin and light dimensions, it can fit tightly around the shaft, achieving an almost seamless fit. This ensures that there is no shaking or eccentricity between the shaft and the deep groove ball bearing during high-speed or low-speed rotation, maximizing the stability of power transmission. 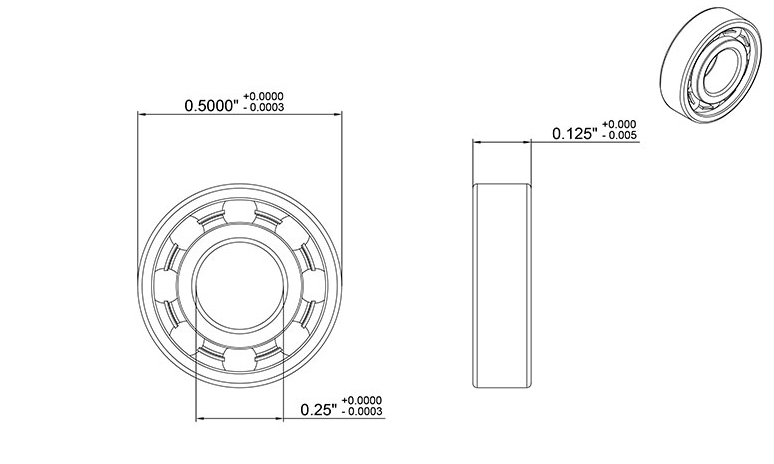
The R188 bearing can be used in the following applications: fidget spinners, glazing machines, pill-making machines, cutting machines, rolling guides, electronic component forming machines, open-circuit chillers, pneumatic welding machines, refractory materials and kilns, air hammers, oil fume purification equipment, mixed-flow pumps, bakery equipment, blister machines, cooking equipment, plate towers, elevators, communications, horizontal rubber machinery, steel mill metallurgy, glass manufacturing, boilers, painting equipment, mining machinery, conveyors, granulators, agricultural machinery, transmission devices, high-speed fans, vacuum equipment, kiln cars, machine tool equipment, construction machinery, conveying equipment, granulators, vibrating screens, automobiles, the petroleum industry, the power industry, electric motors, wind power equipment, and other high-temperature operating machinery.
Maintenance of the R188 Deep Groove Ball Bearing: Key Measures to Ensure Precise Operation
Cleaning
1. Regularly clean external impurities
The R188 deep groove ball bearing is usually applied in precision equipment. Tiny particles such as dust and fibers in its working environment easily adhere to the bearing surface. If these impurities enter the bearing, they may exacerbate wear and affect the normal operation of the bearing. Therefore, it is necessary to clean the bearing regularly.
When cleaning, a clean, soft brush (such as a wool brush) should be used to gently brush away the dust on the bearing surface. For some stubborn dirt, a mild cleaner, such as a special bearing cleaner or anhydrous ethanol, can be used. Drop the cleaner onto a clean soft cloth and then gently wipe the bearing surface. Be careful not to let the cleaner directly touch the sealed part of the bearing, as this may damage the seal and make it easier for impurities to enter the bearing.
2. Importance and methods of internal cleaning
Over time, even with good seals, some impurities may accumulate inside the deep groove ball bearing. When the equipment experiences abnormal vibrations or increased noise, it may be necessary to clean the inside of the bearing.
When disassembling the bearing for internal cleaning, great care must be taken to avoid damaging the bearing. Special bearing disassembly tools can be used, and the correct disassembly steps should be followed. After disassembling the bearing, place it in a clean container and soak it in a clean solvent (such as aviation gasoline or special bearing cleaning oil). The soaking time depends on the severity of the impurities, usually 15 - 30 minutes. After soaking, use clean tweezers or other tools to take out the bearing, and then dry it with clean compressed air or let it air-dry in a clean environment. Before reinstalling the bearing, make sure the inside of the bearing is completely dry and all components are correctly assembled. 
Lubrication Management
1. Select appropriate lubricants
Due to its small size and potentially high operating speed, the R188 bearing has relatively strict requirements for lubricants. Generally, for high-speed operation, grease is recommended. Grease has good adhesion and can form a stable oil film on the bearing surface, reducing friction and wear.
When choosing grease, factors such as the bearing's working temperature, rotational speed, and load should be considered. For example, if the deep groove ball bearing works in a high-temperature environment (such as inside some industrial equipment), high-temperature-resistant grease is required; if the working environment has waterproof requirements (such as outdoor equipment or equipment that may come into contact with liquids), grease with good waterproof performance should be selected. For some equipment with extremely high precision requirements, such as the R188 bearing in precision instruments, grease containing special additives can be used to further improve lubrication performance and antioxidant properties.
2. Correct lubrication methods and intervals
When lubricating the R188 bearing, manual lubrication or an automatic lubrication system can be adopted. For manual lubrication, use a special grease gun to slowly inject grease into the sealed part of the bearing. During the injection process, pay attention to controlling the amount of grease to avoid too much grease entering the bearing, which may increase resistance. Generally, the amount of grease injected each time should be 1/3 - 1/2 of the internal space of the bearing.
The lubrication interval depends on the working conditions of the bearing. If the bearing works in a high-speed, high-temperature, or high-load environment, the lubrication interval should be relatively shortened. For example, for the R188 bearing in some industrial automation equipment, lubrication may be required every 1 - 2 months; while for the R188 bearing in consumer electronics with relatively mild working conditions (such as smart watches), annual lubrication may be sufficient. At the same time, regularly check the state of the grease. If the grease changes color, hardens, or contains impurities, replace it in time. 
Correct Installation and Disassembly
1. Installation precautions
When installing the R188 bearing, ensure that the installation environment is clean. Before installation, clean the shaft and the mounting hole, removing surface oil, rust, and other impurities. At the same time, check whether the dimensions of the shaft and the hole meet the requirements, and their tolerance fits should be within the specified range.
For interference fits, appropriate installation methods should be adopted. The heat installation method or cold installation method can be used. The heat installation method involves heating the bearing to a certain temperature (usually 80 - 100°C higher than the ambient temperature) to expand its inner diameter and then quickly fitting it onto the shaft. The cold installation method is to cool the shaft to a certain temperature (usually -80 - -100°C lower than the ambient temperature) to reduce its outer diameter and then insert it into the bearing inner hole. During the installation process, ensure that the bearing is properly installed, and the fit with the shaft and the hole is tight and has good concentricity.
2. Key points of disassembly
When disassembling the R188 bearing, also be careful to avoid damaging the deep groove ball bearing. For simple disassembly, a small puller tool can be used to slowly pull the bearing out of the shaft or the hole. For tightly installed bearings, special bearing disassembly tools, such as a press, may be required. During disassembly, apply force evenly to avoid excessive local force on the bearing, which may cause deformation. Mark the disassembled bearing, recording information such as its installation position and direction, so that it can be correctly reinstalled.
Operation Status Monitoring
1. Importance of monitoring
By monitoring the operation status of the R188 bearing, abnormalities in the bearing can be detected in time, and maintenance measures can be taken in advance to prevent bearing failures from damaging the equipment. Operation status monitoring mainly includes monitoring the vibration, temperature, and noise of the bearing. 
2. Monitoring methods and tools
Vibration monitoring: A portable vibration analyzer can be used. Install the sensor on the bearing housing or near the bearing to measure parameters such as the vibration amplitude and frequency of the bearing. Under normal circumstances, the vibration amplitude of the R188 bearing is small and the frequency is stable. If the vibration amplitude suddenly increases or the frequency changes, it may indicate problems such as wear, looseness, or imbalance in the bearing.
Temperature monitoring: Use an infrared thermometer or a temperature sensor to monitor the temperature of the bearing in real-time. Under normal working conditions, the bearing temperature should be within a reasonable range. If the temperature is too high, it may be caused by poor lubrication, excessive load, or damage to internal parts.
Noise monitoring: Monitor the noise of the bearing during operation through the human ear or a noise meter. The noise of a normal R188 bearing is small and stable. If abnormal noises, such as sharp whistling or irregular friction sounds, appear, it may indicate a bearing failure. When these abnormal situations are detected, stop the machine immediately for inspection, and repair or replace the bearing.
For more information, feel free to contact QIBR


