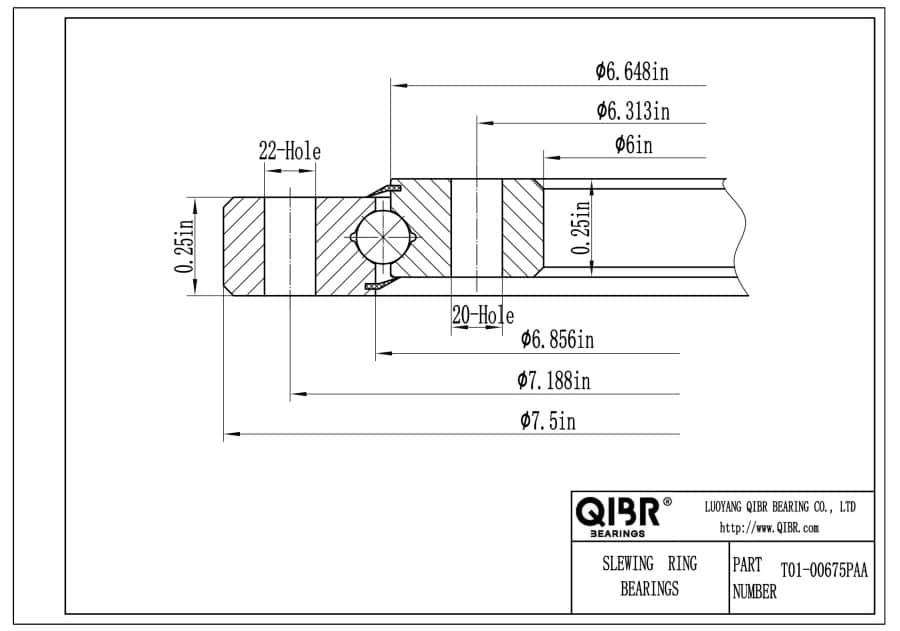
T01-00675PAA
- Inner diameter:
- 6.000 inch
- Outer diameter:
- 7.500 inch
- Width:
- 0.25 inch
- Mass:
- 1.05 lbs
We will provide you with the most suitable solution.
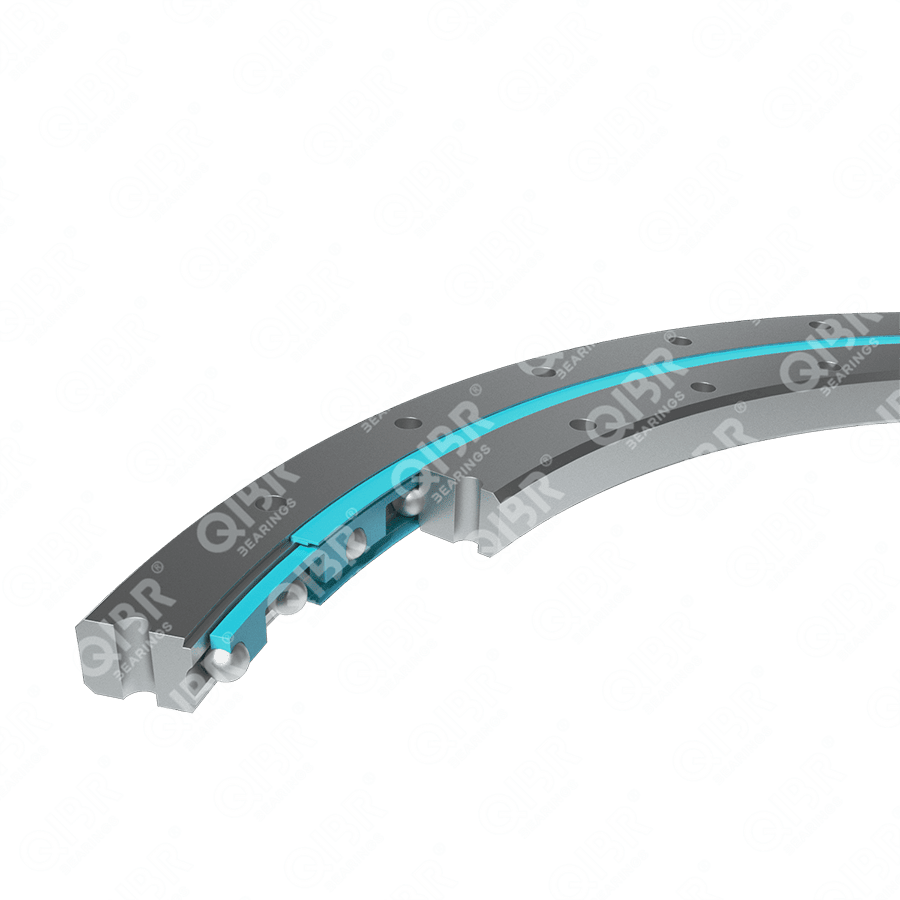
Image may differ from product. See technical specification for details.
Specifications
Seris - T01-00675PAA
Description
QIBR - T01-00675PAA Thin-Section Ball Bearing Advantages and Applications
T01-00675PAA Thin-Section Ball Bearing, high rotation accuracy, low friction, Bore is 6.000 inch,Outer diameter (D) is 7.500 inch,suitable for solar panels, skis, automated production lines and timers, etc., is the most widely used bearing in working conditions requiring high rotation accuracy.
QIBR - T01-00675PAA Thin-Section Ball Bearing Characteristics
T01-00675PAA Thin-Section Ball Bearing, high working efficiency and high running stability. T01-00675PAA Thin-Section Ball Bearing, can bear certain radial load and certain axial load at the same time, suitable for mechanical equipment with high precision requirements.
QIBR - T01-00675PAA Thin section bearing product features and advantages
Lightweight design: Optimize materials and bearing design to reduce bearing weight, occupy less space, and facilitate movement and installation.
High load capacity: It can withstand axial, radial and overturning moments at the same time, suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Excellent running accuracy: Maintain high precision during use and reduce errors in equipment operation.
Efficient friction: Bearing design optimization minimizes friction loss, improves energy transfer efficiency, and reduces energy consumption.
Application: Widely used in lifting machinery, engineering machinery, transportation machinery, mining machinery, metallurgical machinery, medical equipment, ships, warships, radar, wind power generation and other fields.
QIBR - T01-00675PAA Thin section bearing optimization
High-performance materials: Bearing materials can be replaced according to different working conditions, such as stainless steel, ceramics, bearing steel and other materials.
Grease replacement: Provide other coatings such as zinc plating or nickel plating to enhance corrosion resistance and wear resistance and extend its service life in harsh environments.
Structural optimization: By optimizing the bearing structure and geometry, stress concentration is reduced and bearing operation stability is improved.
More customization: QIBR can design and optimize bearings according to customer's load requirements and bearing working environment.
QIBR - T01-00675PAA Thin section bearing quality control
Dimension measurement: Use a variety of professional high-precision instruments to measure multiple dimensions of bearings, with the highest accuracy up to 0.001mm.
Rotation accuracy: Use a micrometer to measure small flaws or deviations on the bearing surface, with a measurement accuracy of up to 0.001mm.
Hardness measurement: Use a hardness tester to measure the surface hardness of the bearing, with a measurement accuracy of up to ±0.5HRC.
Metallographic analysis: Use a professional metallographic microscope to analyze the internal metallographic structure of the metal.
Geometric tolerance: Use a profilometer to measure the bearing geometry and relative position.
Noise monitoring: Use a vibration meter to monitor the vibration during operation and obtain noise data.
Raw material control: Procurement of steel and parts from ISO 14001 certified suppliers to ensure product stability while promoting sustainable development.
Process And PerformanceContent
QIBR - T01-00675PAA Thin-Section Ball Bearings: Manufacturing Process & Performance Indicators
- Material Preparation: Materials (e.g., GCr15 bearing steel, stainless steel, ceramics) are selected per customer requirements. Precision saw cutting ensures a length tolerance of ±0.1mm. Composition is verified via spectrometric analysis, with deviations ≤0.5%.
- Machining Process: Rough turning removes excess material, followed by CNC fine turning with dimensional tolerance ±0.02mm and groove R-angle accuracy ±0.01mm. Bearings are quenched to HRC 58-62, tempered in a vacuum furnace at 180–200°C for 2 hours, and cryogenically treated to ensure dimensional stability (variation ≤0.01%).
- Surface Quality: Superfinishing achieves roughness Ra ≤ 0.05μm, meeting (ABCE 7) P2-grade precision standards.
- Cleanliness: Assembly is conducted in an ISO Class 6 cleanroom using fully synthetic aerospace grease.
- Finished Product Inspection:
- Geometric accuracy is measured via Zeiss PRISMO Ultra CMM (per ISO 10360), with a spatial accuracy of 0.6 + L/600 μm.
- Material microstructure is analyzed using a metallurgical microscope (resolution: 0.15μm).
- Auxiliary Systems & Process Equipment: Vacuum carburizing ensures carburized layer uniformity ≤ ±0.03mm, enhancing fatigue life.
QIBR T01-00675PAA Thin-Section Ball Bearings – R&D Applications
- Cryogenic Bearings:
- Material: Silicon nitride ceramics or special stainless steel composite
- Lubrication: PFPE-based nano-lubricant
- Operating temperature: -200°C to +300°C
- Applications: Spacecraft propulsion systems, superconducting equipment
- Vacuum-Grade Bearings:
- Self-lubricating cage: MoS₂-coated PEEK
- Outgassing rate: <1×10⁻⁷ Torr·L/s/cm²
- Applications: Semiconductor manufacturing equipment, space station robotic arms
- Embedded Sensor Bearings:
- Integrated MEMS microsensors with wireless power transmission
- Energy harvesting efficiency: ≥80%
- Real-time fault diagnosis algorithms
- Applications: Wind turbine main shaft monitoring, high-speed train wheel hubs
- Special-Application Bearings:
- High-temperature, cryogenic, and shock-resistant thin-section bearings
- Applications: Artificial joints, surgical robots
- Ultra-Clean Bearings:
- Designed for dust-free cleanroom environments
- High-Rigidity, Low-Noise Bearings:
- Enhanced motion accuracy for joint systems
- Functional Coating Bearings:
- Custom surface treatments for specialized performance
- Bearings for Difficult-to-Machine Materials:
- Custom solutions for challenging material requirements
As a rolling bearing manufacturer, we specialize in producing ABCE 7 P4-grade and ABCE 9 P2-grade precision bearings for high-speed and heavy-load applications. Our expertise ensures optimal solutions tailored to your needs.
What Do the Prefix Letters for Thin-Section Ball Bearing Materials Mean?
Material designation prefixes vary by brand. For example, KAYDON (US) T01-00675PAA:
- A = AISI 52100 steel & single PTFE seal
- B = AISI 52100 steel & double PTFE seals
- D = AISI 52100 steel & single metal shield
- E = AISI 52100 steel & double metal shields
- F = AISI 52100 steel & single nitrile rubber seal
- G = AISI 52100 steel & double nitrile rubber seals
- H = AISI 52100 steel & single nitrile rubber seal
- J = AISI 52100 steel & double nitrile rubber seals
- K = AISI 52100 steel, unsealed
- L = AISI 52100 steel & double seals
- M = M-50 steel, unsealed
- N = AISI 52100 steel, unsealed
- P = AISI 17-4PH steel & ceramic balls
- Q = AISI 52100 steel, unshielded/unsealed
- S = AISI 440C stainless steel, unsealed
- T = AISI 440C stainless steel & single PTFE seal
- U = AISI 440C stainless steel & double PTFE seals
- V = AISI 440C stainless steel & double metal shields
- W = AISI 440C stainless steel & double nitrile rubber seals
- X = AISI 52100 steel & ceramic balls
- Y = AISI 440C stainless steel & ceramic balls
What Do the Prefix Letters for Thin-Section Bearing Cross-Section Sizes Mean?
Cross-section size prefixes vary by brand. For example, KAYDON (US) T01-00675PAA:
- A = 0.187x0.187 in or 0.250×0.250 in
- B = 0.312×0.312 in
- C = 0.375×0.375 in
- D = 0.500×0.500 in
- E = 0.625×0.625 in
- F = 0.750×0.750 in
- G = 1.000×1.000 in
- H = 0.187×0.250 in or 0.250×0.312 in
- I = 0.312×0.375 in
- J = 0.375×0.437 in
- K = 0.500×0.578 in
- L = 0.625×0.727 in
- M = 0.750×0.875 in
- N = 1.000×1.187 in
- S = 0.187×0.312 in or 0.250×0.375 in
- T = 0.312×0.437 in
- U = 0.375×0.500 in
- V = 0.500×0.656 in
- W = 0.625×0.828 in
- X = 0.750×1.000 in
- Y = 1.000×1.375 in
What Do the Suffix Letters for Thin-Section Bearing Types Mean?
Bearing type suffixes vary by brand. For example, KAYDON (US) T01-00675PAA:
- A = Single angular contact ball bearing
- B = Back-to-back paired set
- C = Deep groove ball bearing
- F = Face-to-face paired set
- T = Tandem paired set
- U = Ground for universal matching
- X = Four-point contact ball bearing
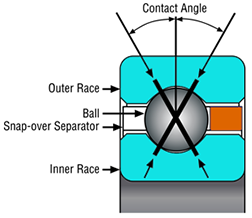
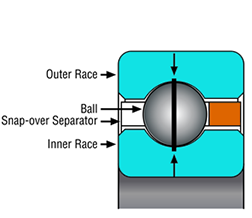
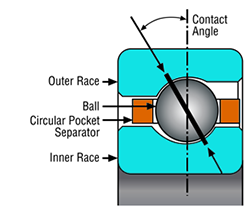
What Do the Suffix Letters for Thin-Section Bearing Cages Mean?
Cage suffixes vary by brand. For example, KAYDON (US) T01-00675PAA:
- C = Non-metallic composite, split, "snap-in"
- D = Phenolic laminated, one-piece, "snap-in"
- E = Brass, split, "snap-in"
- F = Full-complement (no cage)
- G = Nylon, one-piece, round windows
- H = Phenolic laminated, one-piece, round windows
- J = Nylon ribbon cage, round windows
- K = Phenolic laminated, two-piece riveted
- L = Nylon, one-piece "snap-in"
- M = Steel wire raceway, formed strip, "snap-in" (one ball per pocket)
- P = Standard formed, "snap-in"
- Q = PEEK, one-piece, round windows
- R = Standard formed ring, round windows
- S = With spiral spring
- T = Stainless steel, "snap-in" formed ring
- U = Stainless steel, round-window-formed ring
- V = Brass formed ring, "snap-in"
- W = Steel wire raceway, formed strip, "snap-in"
- X = PEEK, one-piece, round windows
- Y = Brass formed ring, round windows
- Z = Spacer rings/blocks/balls
What Do the Precision Suffix Numbers Mean?
Precision grades vary by brand. For example, KAYDON (US) T01-00675PAA:
- 0 = KAYDON Grade 1 (≈ABEC 1F)
- 1 = KAYDON Grade 1, face runout tolerance Grade 4
- 2 = KAYDON Grade 1, face runout tolerance Grade 6
- 3 = KAYDON Grade 3 (≈ABEC 3F)
- 4 = KAYDON Grade 4 (≈ABEC 5F)
- 6 = KAYDON Grade 6 (≈ABEC 7F)
What Do the Internal Fit Suffix Letters Mean?
Internal fit suffixes vary by brand. For example, KAYDON (US) T01-00675PAA:
- A = Clearance 0.0000–0.0005 in
- B = Clearance 0.0000–0.0010 in
- C = Clearance 0.0005–0.0010 in
- D = Clearance 0.0005–0.0015 in
- E = Clearance 0.0010–0.0020 in
- F = Clearance 0.0015–0.0025 in
- G = Clearance 0.0020–0.0030 in
- H = Clearance 0.0030–0.0040 in
- I = Clearance 0.0040–0.0050 in
- J = Clearance 0.0050–0.0060 in
- K = Preload 0.0000–0.0005 in
- L = Preload 0.0000–0.0010 in
- M = Preload 0.0005–0.0010 in
- N = Preload 0.0005–0.0015 in
- P = Preload 0.0010–0.0020 in
- Q = Preload 0.0010–0.0015 in
- R = Preload 0.0015–0.0025 in
- S = Preload 0.0020–0.0030 in
Features & Benefits
Thin-section bearings are a series of bearings designed with limited widths and thicknesses (cross-sections), and each cross-section has a wide range of bore diameters. Most radial ball bearings are designed as the bore diameter increases, the width and thickness of the bearing change proportionally. Thin-section bearings are designed higher efficiency compared to standard bearing sizes, thereby helping to reduce the overall cost of the system. “The cross-section of thin-section bearings remains the same while the bore diameter increases. The thin-section bearing series consists of 12 main cross-section groups, ranging from 3/16″ to 1″, and bore diameters from 1″ to more than 40”. Thin-section bearings are made of 52100 bearing steel or stainless steel material. They can also be plated with chromium. These sizes can be equipped with seals or shields. Thin-section bearings are also made with one of three different contact methods; radial contact, angular contact and four-point contact. These options and a variety of ball and cage types constitute a variety of parts, even when the cross-section of the thin-section bearing series is limited.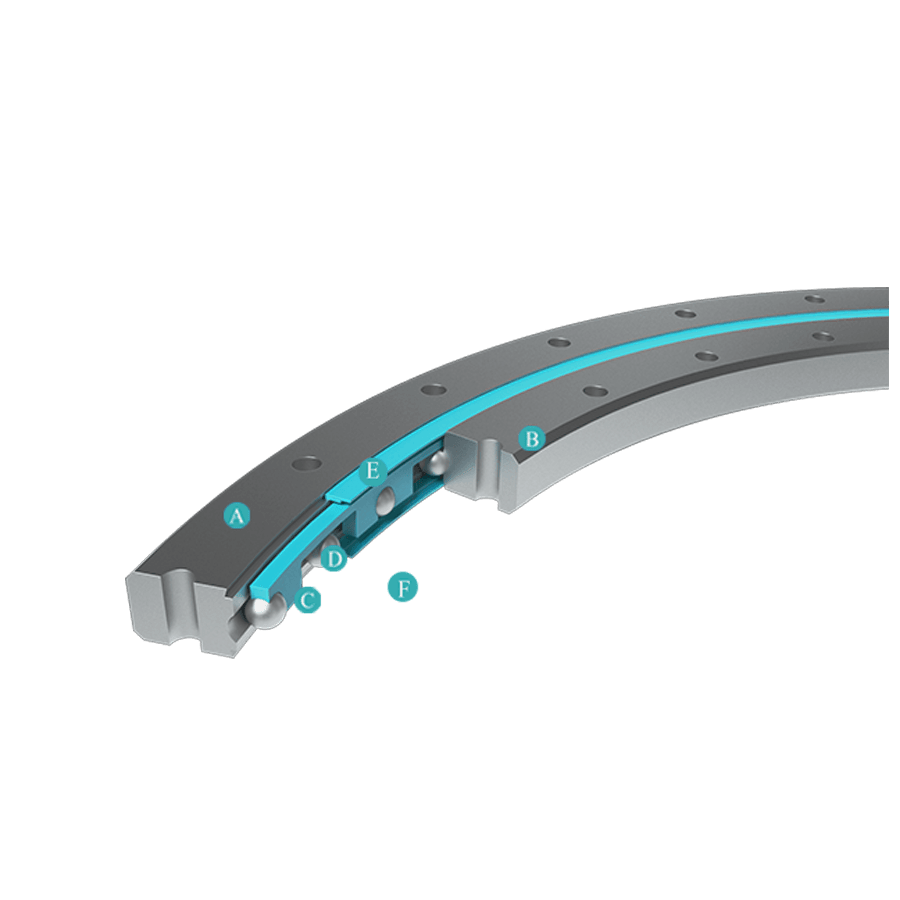
Downloads