QIBR thin section angular contact ball bearings used in robots
- Industry
- Robot manufacturing industry
- Location
- China
- Goals
- Solving the problem of bearing ellipse and warpage out of tolerance, improving product quality and reducing costs
Products used
QIBR thin section angular contact ball bearings used in robots
By improving the processing technology of bearings, solving the problem of bearing ellipse and warpage
Customer introduction:
The BYD brand was born in Shenzhen and established in 1995. Its business spans four major industries: automobiles, rail transit, new energy and electronics. At present, BYD, as the world's leading manufacturer of secondary rechargeable batteries, has covered all core components and assembly businesses of mobile phones in the IT and electronic components industries. The global market share of nickel batteries, lithium batteries for mobile phones, and mobile phone buttons has reached the first place.
a) Challenges (existing problems, why have they not been solved)
With the continuous iteration of products, BYD is preparing to launch its fifth-generation robot arm, but the base speed has not been able to meet the initial design requirements. For this reason, BYD's technical director and purchasing manager found QIBR, hoping to solve the problem with the help of QIBR's R&D strength.
As we all know, high speed, high load and high precision have always been a research and development difficulty for thin-walled corner contacts. To solve this problem, it is necessary to improve and upgrade materials science, production accuracy, and structure, which is a challenge for the entire industry.
b) Solution (How QIBR solves the problem)
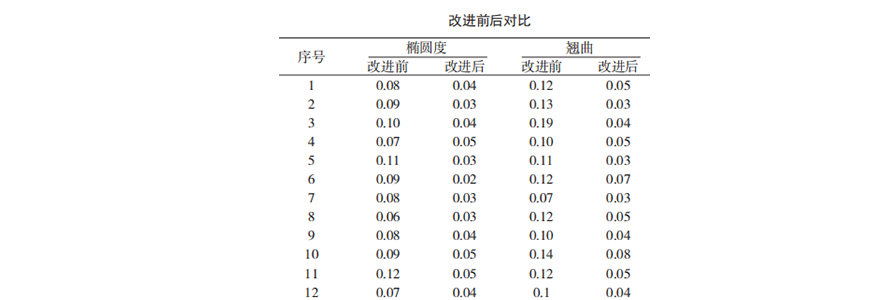
QIBR's technical department used 200 pieces of H76/168TN1/P4.02 as test samples, and detected a 90% scrap rate after traditional processing and heat treatment, of which 43% were due to elliptical deviations and 45% were due to plane warpage deviations.
According to the monitoring and analysis of the bearing processing process and after comparing different lathe processes, it was found that under the same heat treatment process, the qualified rates of bearings with different lathe processes after heat treatment were quite different. The excessive deformation of the original bearing after heat treatment was an important factor causing the difficulty of subsequent grinding.
After research and analysis, QIBR technicians concluded that the tolerance problems of bearing ellipse and warping are mainly caused by the following reasons and made corresponding improvement measures:
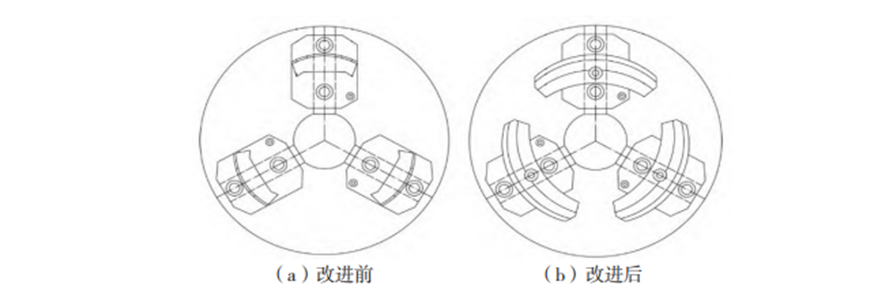
Reason 1: The clamping point of the lathe fixture is too small, causing the thin-walled bearing to be locally subjected to large forces and resulting in original deformation.
Improvement measures: Improve the fixture and design a special fixture to increase the envelope surface with the bearing ring, reduce the pressure per unit area, and thus improve the quality of the machined parts.
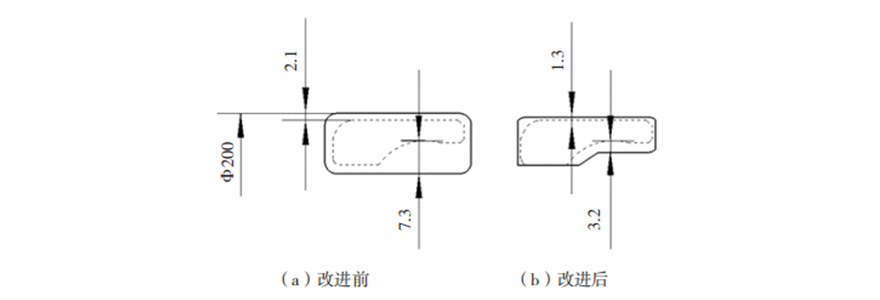
Reason 2: The residual stress of the turned part is too large, and the deformation after stress release due to heat treatment is too large.
Improvement measures:Reduce the amount of residue after rough turning, minimize the deformation after heat treatment, add annealing process after rough turning to significantly reduce the internal stress after rough turning, release the deformation before fine turning, and correct the deformation caused by annealing process during fine turning to improve the dimensional accuracy and stability of the bearing.
Reason 3: In the traditional processing method, the hard turning chamfering process is after the rough grinding of the ring. For thin-walled bearings, this process seriously damages the roundness of the ring, resulting in damage to its processing reference (outer circle), and ultimately produces error reflection, resulting in poor precision after grinding.
Improvement measures: On the basis of improving the turning accuracy, considering the deformation amount of heat treatment and grinding, the chamfering is completed by using a high-precision lathe. Subsequent grinding no longer requires hard turning of each chamfer, which reduces the clamping deformation and cutting deformation caused by turning the chamfer.
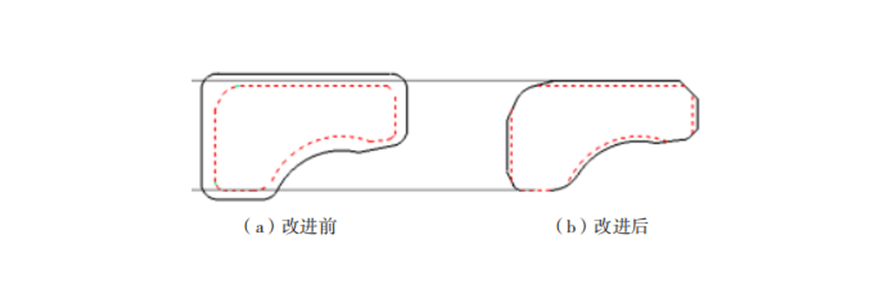
After the above improvement measures, the bearing rings after heat treatment were sampled and the ovality and warpage of the rings were significantly improved before and after the improvement. Based on the improvement measures, the grinding process was also improved, and the hard turning chamfering process, non-critical surface grinding process, and radial grinding force of the rings were reduced. Through the comprehensive improvement of turning and grinding, the qualified rate of the thin-walled angular contact ball bearings for the robot was increased from less than 50% before the improvement to 95%, greatly improving the processing quality.
c) Results
- Optimized product processing quality.
- Improved adjustment accuracy.
- Reduced processing steps.
- Improved work efficiency.
- Reduced labor intensity and processing costs.
Customer Testimonials
When QIBR's technicians communicated with us, our company's technical department put forward requirements for bearings, hoping to solve the problem of bearing failure caused by heat treatment while ensuring the load that the bearing can withstand. QIBR technicians tested the bearings we used before and developed QIBR thin-walled angular contact ball bearings to replace the use of traditional bearings. We conducted actual tests on the installed robots and obtained data consistent with expectations, which perfectly solved the problems of bearing failure due to processing technology, improved the production quality and service life of the robots, and also reduced production costs and damage rates.
The end customers highly praised QIBR, and we will continue to choose QIBR's professional products.
The end customers highly praised QIBR, and we will continue to choose QIBR's professional products.