Newsroom
What is the effect of the contact angle of angular contact bearings
2021-08-29The contact angle of an angular contact ball bearing significantly impacts its lifespan, load capacity, and noise levels. A smaller contact angle typically results in a longer bearing lifespan and greater load capacity, but it may also increase noise. The contact angle of angular contact bearings plays a crucial role in their performance and effectiveness in various applications. Here’s how it influences different aspects:
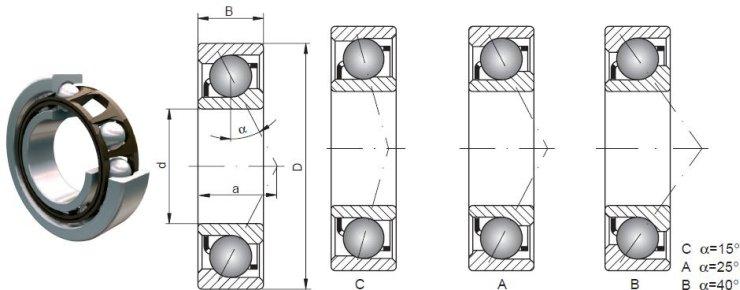
1. Load Capacity:
- Axial and Radial Load Capacity: The contact angle determines the angular contact ball bearing's ability to handle axial and radial loads. Generally, a larger contact angle allows for greater radial load capacity, while a smaller angle enhances axial load capacity. This is due to changes in the contact area and stress distribution between the rolling elements and the raceway.
- Load Tolerance: Angular contact ball bearings with a larger contact angle have higher load tolerance, allowing them to handle greater loads without damage, resulting in a relatively longer lifespan. Conversely, angular contact ball bearings with a smaller contact angle have lower load tolerance and potentially shorter lifespans.
2. Speed and Friction:
- Speed Adaptability: Bearings with a smaller contact angle usually exhibit lower friction and rolling resistance, making them more suitable for high-speed applications. A smaller contact angle reduces the contact area and friction coefficient between the rolling elements and the raceway.
- Operational Stability: Selecting the appropriate contact angle for high-speed operations can enhance bearing stability and reduce vibration and noise.
3. Stiffness:
- Axial and Radial Stiffness: The contact angle also affects the bearing's stiffness. A larger contact angle generally increases both axial and radial stiffness, as it enlarges the contact area and contact stiffness between the rolling elements and the raceway.
- Preload: Bearings require a certain preload during assembly to achieve optimal stiffness. The required preload varies with different contact angles.
4. Precision and Lifespan:
- Precision Requirements: Bearings with a smaller contact angle demand higher manufacturing precision because the concentrated contact points between the rolling elements and the raceway require greater accuracy.
- Lifespan: The contact angle also affects the bearing’s lifespan. On one hand, a larger contact angle can improve load tolerance and durability; on the other, a too-small contact angle may lead to localized high stress at high speeds, potentially causing damage.
5. Applications:
- High-Speed, Light Load Applications: Bearings with a smaller contact angle are suitable due to their lower friction, rolling resistance, and better adaptability.
- Low-Speed, Heavy Load Applications: Bearings with a larger contact angle are preferred as they can handle higher radial loads and provide greater stiffness and stability.
In summary, the contact angle of angular contact bearings significantly impacts load capacity, speed adaptability, stiffness, precision, and lifespan. When selecting an angular contact bearing, it’s essential to choose an appropriate contact angle based on the specific application requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Additionally, it’s advisable to consult the bearing manufacturer's technical manuals and selection guides for more detailed information and recommendations.


