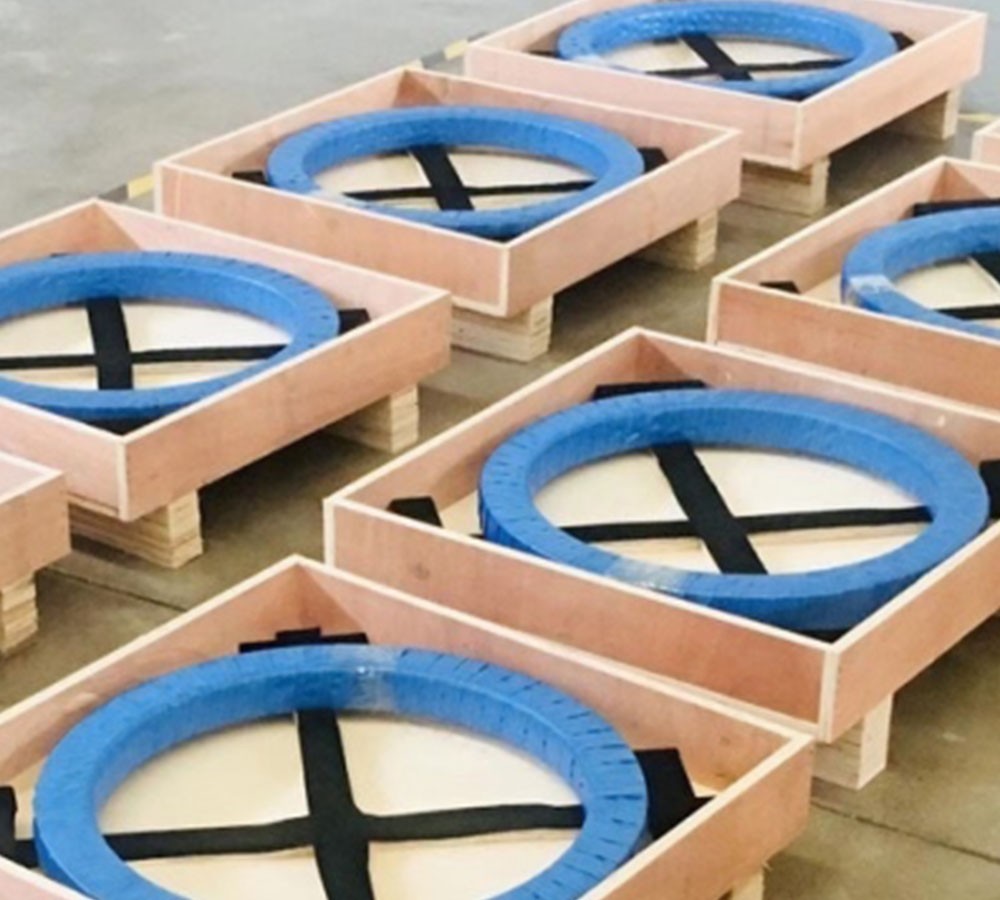
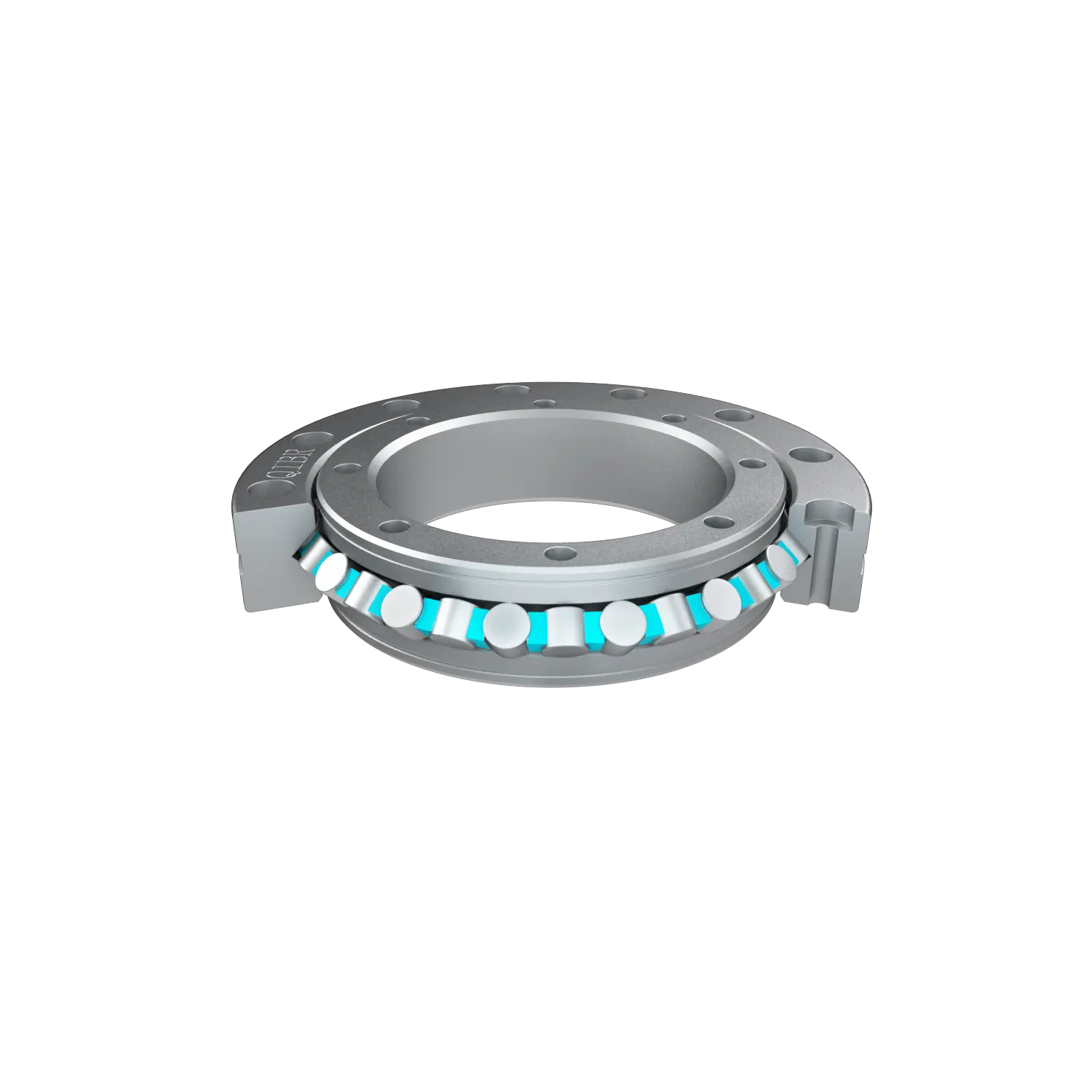
QIBR cross roller bearings were delivered to our customer in Cologne, Germany, to improve the flexibility and work efficiency of robot arm joints
- Continent
- Europe
- Country
- Germany
- Date
- 2016-02-08
- Categories
-
Cross Roller Bearing
- Applications
- Robot arm joints
Products Used
Cross roller bearing
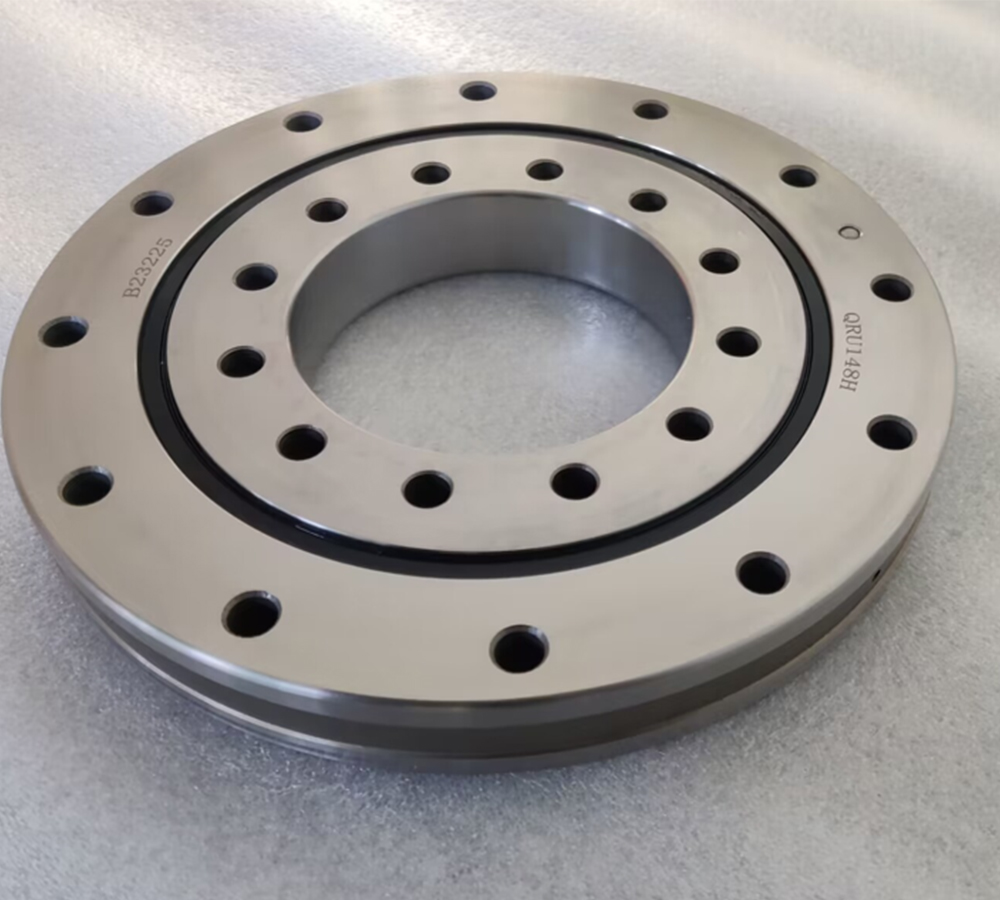
1. High load - bearing capacity : The rolling elements of the QRU148 cross roller bearings are cylindrical rollers arranged in a cross pattern. This allows a single bearing to simultaneously withstand multi-directional loads such as radial loads, axial loads, and overturning moments. The rollers are arranged crosswise at 90°. This structure greatly improves the bearing's load capacity and can maintain stability under high load conditions, making it suitable for use in the joints of robot arms.
2. Excellent durability and reliability : The QRU148 cross roller bearing is made of high-strength steel, which enhances the overall rigidity of the bearing, so that it will not deform significantly when subjected to high loads. It can maintain good stability and performance when the robot arm performs complex movements.
3. Superior rotation accuracy : The manufacturing accuracy of the QRU148 cross roller bearings is high, and the clearance between the rollers is strictly controlled within a very small range. Small clearance enables the bearing to maintain stability and accuracy during operation, ensuring high precision of the bearing during operation, and enabling precise positioning and control.
Additional Notes:
The German customer decided to purchase QRU148 cross roller bearings from QIBR to replace NACHI bearings in order to improve the flexibility and work efficiency of the robot arm joints. The QRU148 cross roller bearing is suitable for medium to high speed applications. The optimized structure enables the QRU148 cross roller bearing to maintain stable performance at high speed rotation, meeting the customer's strict requirements in terms of accuracy, load capacity and service life. This is especially important for robot arm movements that require fast response, allowing the robot arm joints to flexibly respond to various tasks in a dynamic environment.